

Dr. Laurie Starkey
Reactions of Alkenes
Slide Duration:Table of Contents
49m 51s
- Intro0:00
- Organic Chemistry0:07
- Organic0:08
- Inorganic0:26
- Examples of Organic Compounds1:16
- Review Some Chemistry Basics5:23
- Electrons5:42
- Orbitals (s,p,d,f)6:12
- Review Some Chemistry Basics7:35
- Elements & Noble Gases7:36
- Atom & Valance Shell8:47
- Review Some Chemistry Basics11:33
- Electronegative Elements11:34
- Which Is More Electronegative, C or N?13:45
- Ionic & Covalent Bonds14:07
- Ionic Bonds14:08
- Covalent Bonds16:17
- Polar Covalent Bonds19:35
- Polar Covalent Bonds & Electronegativities19:37
- Polarity of Molecules22:56
- Linear molecule23:07
- Bent Molecule23:53
- No Polar Bonds24:21
- Ionic24:52
- Line Drawings26:36
- Line Drawing Overview26:37
- Line Drawing: Example 127:12
- Line Drawing: Example 229:14
- Line Drawing: Example 329:51
- Line Drawing: Example 430:34
- Line Drawing: Example 531:21
- Line Drawing: Example 632:41
- Diversity of Organic Compounds33:57
- Diversity of Organic Compounds33:58
- Diversity of Organic Compounds, cont.39:16
- Diversity of Organic Compounds, cont.39:17
- Examples of Polymers45:26
- Examples of Polymers45:27
44m 25s
- Intro0:00
- Lewis Structures0:08
- How to Draw a Lewis Structure0:09
- Examples2:20
- Lewis Structures6:25
- Examples: Lewis Structure6:27
- Determining Formal Charges8:48
- Example: Determining Formal Charges for Carbon10:11
- Example: Determining Formal Charges for Oxygen11:02
- Lewis Structures12:08
- Typical, Stable Bonding Patterns: Hydrogen12:11
- Typical, Stable Bonding Patterns: Carbon12:58
- Typical, Stable Bonding Patterns: Nitrogen13:25
- Typical, Stable Bonding Patterns: Oxygen13:54
- Typical, Stable Bonding Patterns: Halogen14:16
- Lewis Structure Example15:17
- Drawing a Lewis Structure for Nitric Acid15:18
- Resonance21:58
- Definition of Resonance22:00
- Delocalization22:07
- Hybrid Structure22:38
- Rules for Estimating Stability of Resonance Structures26:04
- Rule Number 1: Complete Octets26:10
- Rule Number 2: Separation of Charge28:13
- Rule Number 3: Negative and Positive Charges30:02
- Rule Number 4: Equivalent31:06
- Looking for Resonance32:09
- Lone Pair Next to a p Bond32:10
- Vacancy Next to a p Bond33:53
- p Bond Between Two Different Elements35:00
- Other Type of Resonance: Benzene36:06
- Resonance Example37:29
- Draw and Rank Resonance Forms37:30
1h 7m 46s
- Intro0:00
- Acid-Base Reactions0:07
- Overview0:08
- Lewis Acid and Lewis Base0:30
- Example 1: Lewis Acid and Lewis Base1:53
- Example 2: Lewis Acid and Lewis Base3:04
- Acid-base Reactions4:54
- Bonsted-Lowry Acid and Bonsted-Lowry Base4:56
- Proton Transfer Reaction5:36
- Acid-Base Equilibrium8:14
- Two Acids in Competition = Equilibrium8:15
- Example: Which is the Stronger Acid?8:40
- Periodic Trends for Acidity12:40
- Across Row12:41
- Periodic Trends for Acidity19:48
- Energy Diagram19:50
- Periodic Trends for Acidity21:28
- Down a Family21:29
- Inductive Effects on Acidity25:52
- Example: Which is the Stronger Acid?25:54
- Other Electron-Withdrawing Group (EWG)30:37
- Inductive Effects on Acidity32:55
- Inductive Effects Decrease with Distance32:56
- Resonance Effects on Acidity36:35
- Examples of Resonance Effects on Acidity36:36
- Resonance Effects on Acidity41:15
- Small and Large Amount of Resonance41:17
- Acid-Base Example43:10
- Which is Most Acidic? Which is the Least Acidic?43:12
- Acid-Base Example49:26
- Which is the Stronger Base?49:27
- Acid-Base Example53:58
- Which is the Strongest Base?53:59
- Common Acids/Bases1:00:45
- Common Acids/Bases1:00:46
- Example: Determine the Direction of Equilibrium1:04:51
1h 23m 35s
- Intro0:00
- Orbitals and Bonding0:20
- Atomic Orbitals (AO)0:21
- Molecular Orbitals (MO)1:46
- Definition of Molecular Orbitals1:47
- Example 1: Formation of Sigma Bond and Molecular Orbitals2:20
- Molecular Orbitals (MO)5:25
- Example 2: Formation of Pi Bond5:26
- Overlapping E Levels of MO's7:28
- Energy Diagram7:29
- Electronic Transitions9:18
- Electronic Transitions9:23
- Hybrid Orbitals12:04
- Carbon AO12:06
- Hybridization13:51
- Hybrid Orbitals15:02
- Examples of Hybrid Orbitals15:05
- Example: Assign Hybridization20:31
- 3-D Sketches24:05
- sp324:24
- sp225:28
- sp27:41
- 3-D Sketches of Molecules29:07
- 3-D Sketches of Molecules 129:08
- 3-D Sketches of Molecules 232:29
- 3-D Sketches of Molecules 335:36
- 3D Sketch37:20
- How to Draw 3D Sketch37:22
- Example 1: Drawing 3D Sketch37:50
- Example 2: Drawing 3D Sketch43:04
- Hybridization and Resonance46:06
- Example: Hybridization and Resonance46:08
- Physical Properties49:55
- Water Solubility, Boiling Points, and Intermolecular Forces49:56
- Types of 'Nonbonding' Interactions51:47
- Dipole-Dipole52:37
- Definition of Dipole-Dipole52:39
- Example: Dipole-Dipole Bonding53:27
- Hydrogen Bonding57:14
- Definition of Hydrogen Bonding57:15
- Example: Hydrogen Bonding58:05
- Van Der Waals/ London Forces1:03:11
- Van Der Waals/ London Forces1:03:12
- Example: Van Der Waals/ London Forces1:04:59
- Water Solubility1:08:32
- Water Solubility1:08:34
- Example: Water Solubility1:09:05
- Example: Acetone1:11:29
- Isomerism1:13:51
- Definition of Isomers1:13:53
- Constitutional Isomers and Example1:14:17
- Stereoisomers and Example1:15:34
- Introduction to Functional Groups1:17:06
- Functional Groups: Example, Abbreviation, and Name1:17:07
- Introduction to Functional Groups1:20:48
- Functional Groups: Example, Abbreviation, and Name1:20:49
1h 13m 38s
- Intro0:00
- Nomenclature of Alkanes0:12
- Nomenclature of Alkanes and IUPAC Rules0:13
- Examples: Nomenclature of Alkanes4:38
- Molecular Formula and Degrees of Unsaturation (DU)17:24
- Alkane Formula17:25
- Example: Heptane17:58
- Why '2n+2' Hydrogens?18:35
- Adding a Ring19:20
- Adding a p Bond19:42
- Example 1: Determine Degrees of Unsaturation (DU)20:17
- Example 2: Determine Degrees of Unsaturation (DU)21:35
- Example 3: Determine DU of Benzene23:30
- Molecular Formula and Degrees of Unsaturation (DU)24:41
- Example 4: Draw Isomers24:42
- Physical properties of Alkanes29:17
- Physical properties of Alkanes29:18
- Conformations of Alkanes33:40
- Conformational Isomers33:42
- Conformations of Ethane: Eclipsed and Staggered34:40
- Newman Projection of Ethane36:15
- Conformations of Ethane40:38
- Energy and Degrees Rotated Diagram40:41
- Conformations of Butane42:28
- Butane42:29
- Newman Projection of Butane43:35
- Conformations of Butane44:25
- Energy and Degrees Rotated Diagram44:30
- Cycloalkanes51:26
- Cyclopropane and Cyclobutane51:27
- Cyclopentane53:56
- Cycloalkanes54:56
- Cyclohexane: Chair, Boat, and Twist Boat Conformations54:57
- Drawing a Cyclohexane Chair57:58
- Drawing a Cyclohexane Chair57:59
- Newman Projection of Cyclohexane1:02:14
- Cyclohexane Chair Flips1:04:06
- Axial and Equatorial Groups1:04:10
- Example: Chair Flip on Methylcyclohexane1:06:44
- Cyclohexane Conformations Example1:09:01
- Chair Conformations of cis-1-t-butyl-4-methylcyclohexane1:09:02
1h 40m 54s
- Intro0:00
- Stereochemistry0:10
- Isomers0:11
- Stereoisomer Examples1:30
- Alkenes1:31
- Cycloalkanes2:35
- Stereoisomer Examples4:00
- Tetrahedral Carbon: Superimposable (Identical)4:01
- Tetrahedral Carbon: Non-Superimposable (Stereoisomers)5:18
- Chirality7:18
- Stereoisomers7:19
- Chiral8:05
- Achiral8:29
- Example: Achiral and Chiral8:45
- Chirality20:11
- Superimposable, Non-Superimposable, Chiral, and Achiral20:12
- Nomenclature23:00
- Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rules23:01
- Nomenclature29:39
- Example 1: Nomenclature29:40
- Example 2: Nomenclature31:49
- Example 3: Nomenclature33:24
- Example 4: Nomenclature35:39
- Drawing Stereoisomers36:58
- Drawing (S)-2-bromopentane36:59
- Drawing the Enantiomer of (S)-2-bromopentane: Method 138:47
- Drawing the Enantiomer of (S)-2-bromopentane: Method 239:35
- Fischer Projections41:47
- Definition of Fischer Projections41:49
- Drawing Fischer Projection43:43
- Use of Fisher Projection: Assigning Configuration49:13
- Molecules with Two Chiral Carbons51:49
- Example A51:42
- Drawing Enantiomer of Example A53:26
- Fischer Projection of A54:25
- Drawing Stereoisomers, cont.59:40
- Drawing Stereoisomers Examples59:41
- Diastereomers1:01:48
- Drawing Stereoisomers1:06:37
- Draw All Stereoisomers of 2,3-dichlorobutane1:06:38
- Molecules with Two Chiral Centers1:10:22
- Draw All Stereoisomers of 2,3-dichlorobutane, cont.1:10:23
- Optical Activity1:14:10
- Chiral Molecules1:14:11
- Angle of Rotation1:14:51
- Achiral Species1:16:46
- Physical Properties of Stereoisomers1:17:11
- Enantiomers1:17:12
- Diastereomers1:18:01
- Example1:18:26
- Physical Properties of Stereoisomers1:23:05
- When Do Enantiomers Behave Differently?1:23:06
- Racemic Mixtures1:28:18
- Racemic Mixtures1:28:21
- Resolution1:29:52
- Unequal Mixtures of Enantiomers1:32:54
- Enantiomeric Excess (ee)1:32:55
- Unequal Mixture of Enantiomers1:34:43
- Unequal Mixture of Enantiomers1:34:44
- Example: Finding ee1:36:38
- Example: Percent of Composition1:39:46
1h 53m 47s
- Intro0:00
- Cycloalkane Nomenclature0:17
- Cycloalkane Nomenclature and Examples0:18
- Alkene Nomenclature6:28
- Alkene Nomenclature and Examples6:29
- Alkene Nomenclature: Stereochemistry15:07
- Alkenes With Two Groups: Cis & Trans15:08
- Alkenes With Greater Than Two Groups: E & Z18:26
- Alkyne Nomenclature24:46
- Alkyne Nomenclature and Examples24:47
- Alkane Has a Higher Priority Than Alkyne28:25
- Alcohol Nomenclature29:24
- Alcohol Nomenclature and Examples29:25
- Alcohol FG Has Priority Over Alkene/yne33:41
- Ether Nomenclature36:32
- Ether Nomenclature and Examples36:33
- Amine Nomenclature42:59
- Amine Nomenclature and Examples43:00
- Amine Nomenclature49:45
- Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary Salt49:46
- Aldehyde Nomenclature51:37
- Aldehyde Nomenclature and Examples51:38
- Ketone Nomenclature58:43
- Ketone Nomenclature and Examples58:44
- Aromatic Nomenclature1:05:02
- Aromatic Nomenclature and Examples1:05:03
- Aromatic Nomenclature, cont.1:09:09
- Ortho, Meta, and Para1:09:10
- Aromatic Nomenclature, cont.1:13:27
- Common Names for Simple Substituted Aromatic Compounds1:13:28
- Carboxylic Acid Nomenclature1:16:35
- Carboxylic Acid Nomenclature and Examples1:16:36
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives1:22:28
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives1:22:42
- General Structure1:23:10
- Acid Halide Nomenclature1:24:48
- Acid Halide Nomenclature and Examples1:24:49
- Anhydride Nomenclature1:28:10
- Anhydride Nomenclature and Examples1:28:11
- Ester Nomenclature1:32:50
- Ester Nomenclature1:32:51
- Carboxylate Salts1:38:51
- Amide Nomenclature1:40:02
- Amide Nomenclature and Examples1:40:03
- Nitrile Nomenclature1:45:22
- Nitrile Nomenclature and Examples1:45:23
51m 1s
- Intro0:00
- Chemical Reactions0:06
- Reactants and Products0:07
- Thermodynamics0:50
- Equilibrium Constant1:06
- Equation2:35
- Organic Reaction3:05
- Energy vs. Progress of Rxn Diagrams3:48
- Exothermic Reaction4:02
- Endothermic Reaction6:54
- Estimating ΔH rxn9:15
- Bond Breaking10:03
- Bond Formation10:25
- Bond Strength11:35
- Homolytic Cleavage11:59
- Bond Dissociation Energy (BDE) Table12:29
- BDE for Multiple Bonds14:32
- Examples17:35
- Kinetics20:35
- Kinetics20:36
- Examples21:49
- Reaction Rate Variables23:15
- Reaction Rate Variables23:16
- Increasing Temperature, Increasing Rate24:08
- Increasing Concentration, Increasing Rate25:39
- Decreasing Energy of Activation, Increasing Rate27:49
- Two-Step Mechanisms30:06
- E vs. POR Diagram (2-step Mechanism)30:07
- Reactive Intermediates33:03
- Reactive Intermediates33:04
- Example: A Carbocation35:20
- Carbocation Stability37:24
- Relative Stability of Carbocation37:25
- Alkyl groups and Hyperconjugation38:45
- Carbocation Stability41:57
- Carbocation Stabilized by Resonance: Allylic41:58
- Carbocation Stabilized by Resonance: Benzylic42:59
- Overall Carbocation Stability44:05
- Free Radicals45:05
- Definition and Examples of Free Radicals45:06
- Radical Mechanisms49:40
- Example: Regular Arrow49:41
- Example: Fish-Hook Arrow50:17
26m 23s
- Intro0:00
- Free Radical Halogenation0:06
- Free Radical Halogenation0:07
- Mechanism: Initiation1:27
- Mechanism: Propagation Steps2:21
- Free Radical Halogenation5:33
- Termination Steps5:36
- Example 1: Terminations Steps6:00
- Example 2: Terminations Steps6:18
- Example 3: Terminations Steps7:43
- Example 4: Terminations Steps8:04
- Regiochemistry of Free Radical Halogenation9:32
- Which Site/Region Reacts and Why?9:34
- Bromination and Rate of Reaction14:03
- Regiochemistry of Free Radical Halogenation14:30
- Chlorination14:31
- Why the Difference in Selectivity?19:58
- Allylic Halogenation20:53
- Examples of Allylic Halogenation20:55
1h 48m 5s
- Intro0:00
- Substitution Reactions0:06
- Substitution Reactions Example0:07
- Nucleophile0:39
- Electrophile1:20
- Leaving Group2:56
- General Reaction4:13
- Substitution Reactions4:43
- General Reaction4:46
- Substitution Reaction Mechanisms: Simultaneous5:08
- Substitution Reaction Mechanisms: Stepwise5:34
- SN2 Substitution6:21
- Example of SN2 Mechanism6:22
- SN2 Kinetics7:58
- Rate of SN29:10
- Sterics Affect Rate of SN29:12
- Rate of SN2 (By Type of RX)14:13
- SN2: E vs. POR Diagram17:26
- E vs. POR Diagram17:27
- Transition State (TS)18:24
- SN2 Transition State, Kinetics20:58
- SN2 Transition State, Kinetics20:59
- Hybridization of TS Carbon21:57
- Example: Allylic LG23:34
- Stereochemistry of SN225:46
- Backside Attack and Inversion of Stereochemistry25:48
- SN2 Summary29:56
- Summary of SN229:58
- Predict Products (SN2)31:42
- Example 1: Predict Products31:50
- Example 2: Predict Products33:38
- Example 3: Predict Products35:11
- Example 4: Predict Products36:11
- Example 5: Predict Products37:32
- SN1 Substitution Mechanism41:52
- Is This Substitution? Could This Be an SN2 Mechanism?41:54
- SN1 Mechanism43:50
- Two Key Steps: 1. Loss of LG43:53
- Two Key Steps: 2. Addition of nu45:11
- SN1 Kinetics47:17
- Kinetics of SN147:18
- Rate of SN1 (By RX type)48:44
- SN1 E vs. POR Diagram49:49
- E vs. POR Diagram49:51
- First Transition Stage (TS-1)51:48
- Second Transition Stage (TS-2)52:56
- Stereochemistry of SN153:44
- Racemization of SN1 and Achiral Carbocation Intermediate53:46
- Example54:29
- SN1 Summary58:25
- Summary of SN158:26
- SN1 or SN2 Mechanisms?1:00:40
- Example 1: SN1 or SN2 Mechanisms1:00:42
- Example 2: SN1 or SN2 Mechanisms1:03:00
- Example 3: SN1 or SN2 Mechanisms1:04:06
- Example 4: SN1 or SN2 Mechanisms1:06:17
- SN1 Mechanism1:09:12
- Three Steps of SN1 Mechanism1:09:13
- SN1 Carbocation Rearrangements1:14:50
- Carbocation Rearrangements Example1:14:51
- SN1 Carbocation Rearrangements1:20:46
- Alkyl Groups Can Also Shift1:20:48
- Leaving Groups1:24:26
- Leaving Groups1:24:27
- Forward or Reverse Reaction Favored?1:26:00
- Leaving Groups1:29:59
- Making poor LG Better: Method 11:30:00
- Leaving Groups1:34:18
- Making poor LG Better: Tosylate (Method 2)1:34:19
- Synthesis Problem1:38:15
- Example: Provide the Necessary Reagents1:38:16
- Nucleophilicity1:41:10
- What Makes a Good Nucleophile?1:41:11
- Nucleophilicity1:44:45
- Periodic Trends: Across Row1:44:47
- Periodic Trends: Down a Family1:46:46
1h 11m 43s
- Intro0:00
- Elimination Reactions: E2 Mechanism0:06
- E2 Mechanism0:08
- Example of E2 Mechanism1:01
- Stereochemistry of E24:48
- Anti-Coplanar & Anti-Elimination4:50
- Example 1: Stereochemistry of E25:34
- Example 2: Stereochemistry of E210:39
- Regiochemistry of E213:04
- Refiochemistry of E2 and Zaitsev's Rule13:05
- Alkene Stability17:39
- Alkene Stability19:20
- Alkene Stability Examples19:22
- Example 1: Draw Both E2 Products and Select Major21:57
- Example 2: Draw Both E2 Products and Select Major25:02
- SN2 Vs. E2 Mechanisms29:06
- SN2 Vs. E2 Mechanisms29:07
- When Do They Compete?30:34
- SN2 Vs. E2 Mechanisms31:23
- Compare Rates31:24
- SN2 Vs. E2 Mechanisms36:34
- t-BuBr: What If Vary Base?36:35
- Preference for E2 Over SN2 (By RX Type)40:42
- E1 Elimination Mechanism41:51
- E1 - Elimination Unimolecular41:52
- E1 Mechanism: Step 144:14
- E1 Mechanism: Step 244:48
- E1 Kinetics46:58
- Rate = k[RCI]47:00
- E1 Rate (By Type of Carbon Bearing LG)48:31
- E1 Stereochemistry49:49
- Example 1: E1 Stereochemistry49:51
- Example 2: E1 Stereochemistry52:31
- Carbocation Rearrangements55:57
- Carbocation Rearrangements56:01
- Product Mixtures57:20
- Predict the Product: SN2 vs. E259:58
- Example 1: Predict the Product1:00:00
- Example 2: Predict the Product1:02:10
- Example 3: Predict the Product1:04:07
- Predict the Product: SN2 vs. E21:06:06
- Example 4: Predict the Product1:06:07
- Example 5: Predict the Product1:07:29
- Example 6: Predict the Product1:07:51
- Example 7: Predict the Product1:09:18
36m 39s
- Intro0:00
- Alkenes0:12
- Definition and Structure of Alkenes0:13
- 3D Sketch of Alkenes1:53
- Pi Bonds3:48
- Alkene Stability4:57
- Alkyl Groups Attached4:58
- Trans & Cis6:20
- Alkene Stability8:42
- Pi Bonds & Conjugation8:43
- Bridgehead Carbons & Bredt's Rule10:22
- Measuring Stability: Hydrogenation Reaction11:40
- Alkene Synthesis12:01
- Method 1: E2 on Alkyl Halides12:02
- Review: Stereochemistry16:17
- Review: Regiochemistry16:50
- Review: SN2 vs. E217:34
- Alkene Synthesis18:57
- Method 2: Dehydration of Alcohols18:58
- Mechanism20:08
- Alkene Synthesis23:26
- Alcohol Dehydration23:27
- Example 1: Comparing Strong Acids26:59
- Example 2: Mechanism for Dehydration Reaction29:00
- Example 3: Transform32:50
2h 8m 44s
- Intro0:00
- Reactions of Alkenes0:05
- Electrophilic Addition Reaction0:06
- Addition of HX2:02
- Example: Regioselectivity & 2 Steps Mechanism2:03
- Markovnikov Addition5:30
- Markovnikov Addition is Favored5:31
- Graph: E vs. POR6:33
- Example8:29
- Example: Predict and Consider the Stereochemistry8:30
- Hydration of Alkenes12:31
- Acid-catalyzed Addition of Water12:32
- Strong Acid14:20
- Hydration of Alkenes15:20
- Acid-catalyzed Addition of Water: Mechanism15:21
- Hydration vs. Dehydration19:51
- Hydration Mechanism is Exact Reverse of Dehydration19:52
- Example21:28
- Example: Hydration Reaction21:29
- Alternative 'Hydration' Methods25:26
- Oxymercuration-Demercuration25:27
- Oxymercuration Mechanism28:55
- Mechanism of Oxymercuration28:56
- Alternative 'Hydration' Methods30:51
- Hydroboration-Oxidation30:52
- Hydroboration Mechanism33:22
- 1-step (concerted)33:23
- Regioselective34:45
- Stereoselective35:30
- Example35:58
- Example: Hydroboration-Oxidation35:59
- Example40:42
- Example: Predict the Major Product40:43
- Synthetic Utility of 'Alternate' Hydration Methods44:36
- Example: Synthetic Utility of 'Alternate' Hydration Methods44:37
- Flashcards47:28
- Tips On Using Flashcards47:29
- Bromination of Alkenes49:51
- Anti-Addition of Br₂49:52
- Bromination Mechanism53:16
- Mechanism of Bromination53:17
- Bromination Mechanism55:42
- Mechanism of Bromination55:43
- Bromination: Halohydrin Formation58:54
- Addition of other Nu: to Bromonium Ion58:55
- Mechanism1:00:08
- Halohydrin: Regiochemistry1:03:55
- Halohydrin: Regiochemistry1:03:56
- Bromonium Ion Intermediate1:04:26
- Example1:09:28
- Example: Predict Major Product1:09:29
- Example Cont.1:10:59
- Example: Predict Major Product Cont.1:11:00
- Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes1:13:19
- Features of Catalytic Hydrogenation1:13:20
- Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes1:14:48
- Metal Surface1:14:49
- Heterogeneous Catalysts1:15:29
- Homogeneous Catalysts1:16:08
- Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes1:17:44
- Hydrogenation & Pi Bond Stability1:17:45
- Energy Diagram1:19:22
- Catalytic Hydrogenation of Dienes1:20:40
- Hydrogenation & Pi Bond Stability1:20:41
- Energy Diagram1:23:31
- Example1:24:14
- Example: Predict Product1:24:15
- Oxidation of Alkenes1:27:21
- Redox Review1:27:22
- Epoxide1:30:26
- Diol (Glycol)1:30:54
- Ketone/ Aldehyde1:31:13
- Epoxidation1:32:08
- Epoxidation1:32:09
- General Mechanism1:36:32
- Alternate Epoxide Synthesis1:37:38
- Alternate Epoxide Synthesis1:37:39
- Dihydroxylation1:41:10
- Dihydroxylation1:41:12
- General Mechanism (Concerted Via Cycle Intermediate)1:42:38
- Ozonolysis1:44:22
- Ozonolysis: Introduction1:44:23
- Ozonolysis: Is It Good or Bad?1:45:05
- Ozonolysis Reaction1:48:54
- Examples1:51:10
- Example 1: Ozonolysis1:51:11
- Example1:53:25
- Radical Addition to Alkenes1:55:05
- Recall: Free-Radical Halogenation1:55:15
- Radical Mechanism1:55:45
- Propagation Steps1:58:01
- Atom Abstraction1:58:30
- Addition to Alkene1:59:11
- Radical Addition to Alkenes1:59:54
- Markovnivok (Electrophilic Addition) & anti-Mark. (Radical Addition)1:59:55
- Mechanism2:01:03
- Alkene Polymerization2:05:35
- Example: Alkene Polymerization2:05:36
1h 13m 19s
- Intro0:00
- Structure of Alkynes0:04
- Structure of Alkynes0:05
- 3D Sketch2:30
- Internal and Terminal4:03
- Reductions of Alkynes4:36
- Catalytic Hydrogenation4:37
- Lindlar Catalyst5:25
- Reductions of Alkynes7:24
- Dissolving Metal Reduction7:25
- Oxidation of Alkynes9:24
- Ozonolysis9:25
- Reactions of Alkynes10:56
- Addition Reactions: Bromination10:57
- Addition of HX12:24
- Addition of HX12:25
- Addition of HX13:36
- Addition of HX: Mechanism13:37
- Example17:38
- Example: Transform17:39
- Hydration of Alkynes23:35
- Hydration of Alkynes23:36
- Hydration of Alkynes26:47
- Hydration of Alkynes: Mechanism26:49
- 'Hydration' via Hydroboration-Oxidation32:57
- 'Hydration' via Hydroboration-Oxidation32:58
- Disiamylborane33:28
- Hydroboration-Oxidation Cont.34:25
- Alkyne Synthesis36:17
- Method 1: Alkyne Synthesis By Dehydrohalogenation36:19
- Alkyne Synthesis39:06
- Example: Transform39:07
- Alkyne Synthesis41:21
- Method 2 & Acidity of Alkynes41:22
- Conjugate Bases43:06
- Preparation of Acetylide Anions49:55
- Preparation of Acetylide Anions49:57
- Alkyne Synthesis53:40
- Synthesis Using Acetylide Anions53:41
- Example 1: Transform57:04
- Example 2: Transform1:01:07
- Example 3: Transform1:06:22
59m 52s
- Intro0:00
- Alcohols0:11
- Attributes of Alcohols0:12
- Boiling Points2:00
- Water Solubility5:00
- Water Solubility (Like Dissolves Like)5:01
- Acidity of Alcohols9:39
- Comparison of Alcohols Acidity9:41
- Preparation of Alkoxides13:03
- Using Strong Base Like Sodium Hydride13:04
- Using Redox Reaction15:36
- Preparation of Alkoxides17:41
- Using K°17:42
- Phenols Are More Acidic Than Other Alcohols19:51
- Synthesis of Alcohols, ROH21:43
- Synthesis of Alcohols from Alkyl Halides, RX (SN2 or SN1)21:44
- Synthesis of Alcohols, ROH25:08
- Unlikely on 2° RX (E2 Favored)25:09
- Impossible on 3° RX (E2) and Phenyl/Vinyl RX (N/R)25:47
- Synthesis of Alcohols, ROH26:26
- SN1 with H₂O 'Solvolysis' or 'Hydrolysis'26:27
- Carbocation Can Rearrange29:00
- Synthesis of Alcohols, ROH30:08
- Synthesis of Alcohols From Alkenes: Hydration30:09
- Synthesis of Alcohols From Alkenes: Oxidation/Diol32:20
- Synthesis of Alcohols, ROH33:14
- Synthesis of Alcohols From Ketones and Aldehydes33:15
- Organometallic Reagents: Preparation37:03
- Grignard (RMgX)37:04
- Organolithium (Rli)40:03
- Organometallic Reagents: Reactions41:45
- Reactions of Organometallic Reagents41:46
- Organometallic Reagents: Reactions as Strong Nu:46:40
- Example 1: Reactions as Strong Nu:46:41
- Example 2: Reactions as Strong Nu:48:57
- Hydride Nu:50:52
- Hydride Nu:50:53
- Examples53:34
- Predict 153:35
- Predict 254:45
- Examples56:43
- Transform56:44
- Provide Starting Material58:18
45m 35s
- Intro0:00
- Oxidation Reactions0:08
- Oxidizing Agents: Jones, PCC, Swern0:09
- 'Jones' Oxidation0:43
- Example 1: Predict Oxidation Reactions2:29
- Example 2: Predict Oxidation Reactions3:00
- Oxidation Reactions4:11
- Selective Oxidizing Agents (PCC and Swern)4:12
- PCC (Pyridiniym Chlorochromate)5:10
- Swern Oxidation6:05
- General [ox] Mechanism8:32
- General [ox] Mechanism8:33
- Oxidation of Alcohols10:11
- Example 1: Oxidation of Alcohols10:12
- Example 2: Oxidation of Alcohols11:20
- Example 3: Oxidation of Alcohols11:46
- Example13:09
- Predict: PCC Oxidation Reactions13:10
- Tosylation of Alcohols15:22
- Introduction to Tosylation of Alcohols15:23
- Example21:08
- Example: Tosylation of Alcohols21:09
- Reductions of Alcohols23:39
- Reductions of Alcohols via SN2 with Hydride24:22
- Reductions of Alcohols via Dehydration27:12
- Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl Halides30:12
- Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl Halides via Tosylate30:13
- Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl Halides31:17
- Using HX31:18
- Mechanism32:09
- Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl Halides35:43
- Reagents that Provide LG and Nu: in One 'Pot'35:44
- General Mechanisms37:44
- Example 1: General Mechanisms37:45
- Example 2: General Mechanisms39:25
- Example41:04
- Transformation of Alcohols41:05
1h 34m 45s
- Intro0:00
- Ethers0:11
- Overview of Ethers0:12
- Boiling Points1:37
- Ethers4:34
- Water Solubility (Grams per 100mL H₂O)4:35
- Synthesis of Ethers7:53
- Williamson Ether Synthesis7:54
- Example: Synthesis of Ethers9:23
- Synthesis of Ethers10:27
- Example: Synthesis of Ethers10:28
- Intramolecular SN213:04
- Planning an Ether Synthesis14:45
- Example 1: Planning an Ether Synthesis14:46
- Planning an Ether Synthesis16:16
- Example 2: Planning an Ether Synthesis16:17
- Planning an Ether Synthesis22:04
- Example 3: Synthesize Dipropyl Ether22:05
- Planning an Ether Synthesis26:01
- Example 4: Transform26:02
- Synthesis of Epoxides30:05
- Synthesis of Epoxides Via Williamson Ether Synthesis30:06
- Synthesis of Epoxides Via Oxidation32:42
- Reaction of Ethers33:35
- Reaction of Ethers33:36
- Reactions of Ethers with HBr or HI34:44
- Reactions of Ethers with HBr or HI34:45
- Mechanism35:25
- Epoxide Ring-Opening Reaction39:25
- Epoxide Ring-Opening Reaction39:26
- Example: Epoxide Ring-Opening Reaction42:42
- Acid-Catalyzed Epoxide Ring Opening44:16
- Acid-Catalyzed Epoxide Ring Opening Mechanism44:17
- Acid-Catalyzed Epoxide Ring Opening50:13
- Acid-Catalyzed Epoxide Ring Opening Mechanism50:14
- Catalyst Needed for Ring Opening53:34
- Catalyst Needed for Ring Opening53:35
- Stereochemistry of Epoxide Ring Opening55:56
- Stereochemistry: SN2 Mechanism55:57
- Acid or Base Mechanism?58:30
- Example1:01:03
- Transformation1:01:04
- Regiochemistry of Epoxide Ring Openings1:05:29
- Regiochemistry of Epoxide Ring Openings in Base1:05:30
- Regiochemistry of Epoxide Ring Openings in Acid1:07:34
- Example1:10:26
- Example 1: Epoxide Ring Openings in Base1:10:27
- Example 2: Epoxide Ring Openings in Acid1:12:50
- Reactions of Epoxides with Grignard and Hydride1:15:35
- Reactions of Epoxides with Grignard and Hydride1:15:36
- Example1:21:47
- Example: Ethers1:21:50
- Example1:27:01
- Example: Synthesize1:27:02
16m 50s
- Intro0:00
- Thiols and Thioethers0:10
- Physical Properties0:11
- Reactions Can Be Oxidized2:16
- Acidity of Thiols3:11
- Thiols Are More Acidic Than Alcohols3:12
- Synthesis of Thioethers6:44
- Synthesis of Thioethers6:45
- Example8:43
- Example: Synthesize the Following Target Molecule8:44
- Example14:18
- Example: Predict14:19
2h 18m 12s
- Intro0:00
- Aldehydes & Ketones0:11
- The Carbonyl: Resonance & Inductive0:12
- Reactivity0:50
- The Carbonyl2:35
- The Carbonyl2:36
- Carbonyl FG's4:10
- Preparation/Synthesis of Aldehydes & Ketones6:18
- Oxidation of Alcohols6:19
- Ozonolysis of Alkenes7:16
- Hydration of Alkynes8:01
- Reaction with Hydride Nu:9:00
- Reaction with Hydride Nu:9:01
- Reaction with Carbon Nu:11:29
- Carbanions: Acetylide11:30
- Carbanions: Cyanide14:23
- Reaction with Carbon Nu:15:32
- Organometallic Reagents (RMgX, Rli)15:33
- Retrosynthesis of Alcohols17:04
- Retrosynthesis of Alcohols17:05
- Example19:30
- Example: Transform19:31
- Example22:57
- Example: Transform22:58
- Example28:19
- Example: Transform28:20
- Example33:36
- Example: Transform33:37
- Wittig Reaction37:39
- Wittig Reaction: A Resonance-Stabilized Carbanion (Nu:)37:40
- Wittig Reaction: Mechanism39:51
- Preparation of Wittig Reagent41:58
- Two Steps From RX41:59
- Example: Predict45:02
- Wittig Retrosynthesis46:19
- Wittig Retrosynthesis46:20
- Synthesis48:09
- Reaction with Oxygen Nu:51:21
- Addition of H₂O51:22
- Exception: Formaldehyde is 99% Hydrate in H₂O Solution54:10
- Exception: Hydrate is Favored if Partial Positive Near Carbonyl55:26
- Reaction with Oxygen Nu:57:45
- Addition of ROH57:46
- TsOH: Tosic Acid58:28
- Addition of ROH Cont.59:09
- Example1:01:43
- Predict1:01:44
- Mechanism1:03:08
- Mechanism for Acetal Formation1:04:10
- Mechanism for Acetal Formation1:04:11
- What is a CTI?1:15:04
- Tetrahedral Intermediate1:15:05
- Charged Tetrahedral Intermediate1:15:45
- CTI: Acid-cat1:16:10
- CTI: Base-cat1:17:01
- Acetals & Cyclic Acetals1:17:49
- Overall1:17:50
- Cyclic Acetals1:18:46
- Hydrolysis of Acetals: Regenerates Carbonyl1:20:01
- Hydrolysis of Acetals: Regenerates Carbonyl1:20:02
- Mechanism1:22:08
- Reaction with Nitrogen Nu:1:30:11
- Reaction with Nitrogen Nu:1:30:12
- Example1:32:18
- Mechanism of Imine Formation1:33:24
- Mechanism of Imine Formation1:33:25
- Oxidation of Aldehydes1:38:12
- Oxidation of Aldehydes 11:38:13
- Oxidation of Aldehydes 21:39:52
- Oxidation of Aldehydes 31:40:10
- Reductions of Ketones and Aldehydes1:40:54
- Reductions of Ketones and Aldehydes1:40:55
- Hydride/ Workup1:41:22
- Raney Nickel1:42:07
- Reductions of Ketones and Aldehydes1:43:24
- Clemmensen Reduction & Wolff-Kishner Reduction1:43:40
- Acetals as Protective Groups1:46:50
- Acetals as Protective Groups1:46:51
- Example1:50:39
- Example: Consider the Following Synthesis1:50:40
- Protective Groups1:54:47
- Protective Groups1:54:48
- Example1:59:02
- Example: Transform1:59:03
- Example: Another Route2:04:54
- Example: Transform2:08:49
- Example2:08:50
- Transform2:08:51
- Example2:11:05
- Transform2:11:06
- Example2:13:45
- Transform2:13:46
- Example2:15:43
- Provide the Missing Starting Material2:15:44
38m 58s
- Intro0:00
- Practice Problems0:33
- Practice Problem 1: Transform0:34
- Practice Problem 2: Transform3:57
- Practice Problems7:49
- Practice Problem 3: Transform7:50
- Practice Problems15:32
- Practice Problem 4: Transform15:34
- Practice Problem 5: Transform20:15
- Practice Problems24:08
- Practice Problem 6: Transform24:09
- Practice Problem 7: Transform29:27
- Practice Problems33:08
- Practice Problem 8: Transform33:09
- Practice Problem 9: Transform35:23
1h 17m 51s
- Intro0:00
- Review Reactions of Ketone/Aldehyde0:06
- Carbonyl Reactivity0:07
- Nu: = Hydride (Reduction)1:37
- Nu: = Grignard2:08
- Review Reactions of Ketone/Aldehyde2:53
- Nu: = Alcohol2:54
- Nu: = Amine3:46
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives4:37
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives4:38
- Ketone vs. Ester Reactivity6:33
- Ketone Reactivity6:34
- Ester Reactivity6:55
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives7:30
- Acid Halide, Anhydride, Ester, Amide, and Nitrile7:43
- General Reactions of Acarboxylic Acid Derivatives9:22
- General Reactions of Acarboxylic Acid Derivatives9:23
- Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids12:16
- Acetic Acid12:17
- Carboxylic Acids15:46
- Aciditiy of Carboxylic Acids, RCO₂H17:45
- Alcohol17:46
- Carboxylic Acid19:21
- Aciditiy of Carboxylic Acids, RCO₂H21:31
- Aciditiy of Carboxylic Acids, RCO₂H21:32
- Aciditiy of Carboxylic Acids, RCO₂H24:48
- Example: Which is the Stronger Acid?24:49
- Aciditiy of Carboxylic Acids, RCO₂H30:06
- Inductive Effects Decrease with Distance30:07
- Preparation of Carboxylic Acids, RCO₂H31:55
- A) By Oxidation31:56
- Preparation of Carboxylic Acids, RCO₂H34:37
- Oxidation of Alkenes/Alkynes - Ozonolysis34:38
- Preparation of Carboxylic Acids, RCO₂H36:17
- B) Preparation of RCO₂H from Organometallic Reagents36:18
- Preparation of Carboxylic Acids, RCO₂H38:02
- Example: Preparation of Carboxylic Acids38:03
- Preparation of Carboxylic Acids, RCO₂H40:38
- C) Preparation of RCO₂H by Hydrolysis of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives40:39
- Hydrolysis Mechanism42:19
- Hydrolysis Mechanism42:20
- Mechanism: Acyl Substitution (Addition/Elimination)43:05
- Hydrolysis Mechanism47:27
- Substitution Reaction47:28
- RO is Bad LG for SN1/SN247:39
- RO is okay LG for Collapse of CTI48:31
- Hydrolysis Mechanism50:07
- Base-promoted Ester Hydrolysis (Saponification)50:08
- Applications of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives:53:10
- Saponification Reaction53:11
- Ester Hydrolysis57:15
- Acid-Catalyzed Mechanism57:16
- Ester Hydrolysis Requires Acide or Base1:03:06
- Ester Hydrolysis Requires Acide or Base1:03:07
- Nitrile Hydrolysis1:05:22
- Nitrile Hydrolysis1:05:23
- Nitrile Hydrolysis Mechanism1:06:53
- Nitrile Hydrolysis Mechanism1:06:54
- Use of Nitriles in Synthesis1:12:39
- Example: Nitirles in Synthesis1:12:40
1h 21m 4s
- Intro0:00
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives0:05
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives0:06
- General Structure1:00
- Preparation of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives1:19
- Which Carbonyl is the Better E+?1:20
- Inductive Effects1:54
- Resonance3:23
- Preparation of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives6:52
- Which is Better E+, Ester or Acid Chloride?6:53
- Inductive Effects7:02
- Resonance7:20
- Preparation of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives10:45
- Which is Better E+, Carboxylic Acid or Anhydride?10:46
- Inductive Effects & Resonance11:00
- Overall: Order of Electrophilicity and Leaving Group14:49
- Order of Electrophilicity and Leaving Group14:50
- Example: Acid Chloride16:26
- Example: Carboxylate19:17
- Carboxylic Acid Derivative Interconversion20:53
- Carboxylic Acid Derivative Interconversion20:54
- Preparation of Acid Halides24:31
- Preparation of Acid Halides24:32
- Preparation of Anhydrides25:45
- A) Dehydration of Acids (For Symmetrical Anhydride)25:46
- Preparation of Anhydrides27:29
- Example: Dehydration of Acids27:30
- Preparation of Anhydrides29:16
- B) From an Acid Chloride (To Make Mixed Anhydride)29:17
- Mechanism30:03
- Preparation of Esters31:53
- A) From Acid Chloride or Anhydride31:54
- Preparation of Esters33:48
- B) From Carboxylic Acids (Fischer Esterification)33:49
- Mechanism36:55
- Preparations of Esters41:38
- Example: Predict the Product41:39
- Preparation of Esters43:17
- C) Transesterification43:18
- Mechanism45:17
- Preparation of Esters47:58
- D) SN2 with Carboxylate47:59
- Mechanism: Diazomethane49:28
- Preparation of Esters51:01
- Example: Transform51:02
- Preparation of Amides52:27
- A) From an Acid Cl or Anhydride52:28
- Preparations of Amides54:47
- B) Partial Hydrolysis of Nitriles54:48
- Preparation of Amides56:11
- Preparation of Amides: Find Alternate Path56:12
- Preparation of Amides59:04
- C) Can't be Easily Prepared from RCO₂H Directly59:05
- Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives with Nucleophiles1:01:41
- A) Hydride Nu: Review1:01:42
- A) Hydride Nu: Sodium Borohydride + Ester1:02:43
- Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives with Nucleophiles1:03:57
- Lithium Aluminum Hydride (LAH)1:03:58
- Mechanism1:04:29
- Summary of Hydride Reductions1:07:09
- Summary of Hydride Reductions 11:07:10
- Summary of Hydride Reductions 21:07:36
- Hydride Reduction of Amides1:08:12
- Hydride Reduction of Amides Mechanism1:08:13
- Reaction of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives with Organometallics1:12:04
- Review 11:12:05
- Review 21:12:50
- Reaction of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives with Organometallics1:14:22
- Example: Lactone1:14:23
- Special Hydride Nu: Reagents1:16:34
- Diisobutylaluminum Hydride1:16:35
- Example1:17:25
- Other Special Hydride1:18:41
- Addition of Organocuprates to Acid Chlorides1:19:07
- Addition of Organocuprates to Acid Chlorides1:19:08
1h 26m 22s
- Intro0:00
- Enols and Enolates0:09
- The Carbonyl0:10
- Keto-Enol Tautomerization1:17
- Keto-Enol Tautomerization Mechanism2:28
- Tautomerization Mechanism (2 Steps)2:29
- Keto-Enol Tautomerization Mechanism5:15
- Reverse Reaction5:16
- Mechanism6:07
- Formation of Enolates7:27
- Why is a Ketone's α H's Acidic?7:28
- Formation of Other Carbanions10:05
- Alkyne10:06
- Alkane and Alkene10:53
- Formation of an Enolate: Choice of Base11:27
- Example: Choice of Base11:28
- Formation of an Enolate: Choice of Base13:56
- Deprotonate, Stronger Base, and Lithium Diisopropyl Amide (LDA)13:57
- Formation of an Enolate: Choice of Base15:48
- Weaker Base & 'Active' Methylenes15:49
- Why Use NaOEt instead of NaOH?19:01
- Other Acidic 'α' Protons20:30
- Other Acidic 'α' Protons20:31
- Why is an Ester Less Acidic than a Ketone?24:10
- Other Acidic 'α' Protons25:19
- Other Acidic 'α' Protons Continue25:20
- How are Enolates Used25:54
- Enolates25:55
- Possible Electrophiles26:21
- Alkylation of Enolates27:56
- Alkylation of Enolates27:57
- Resonance Form30:03
- α-Halogenation32:17
- α-Halogenation32:18
- Iodoform Test for Methyl Ketones33:47
- α-Halogenation35:55
- Acid-Catalyzed35:57
- Mechanism: 1st Make Enol (2 Steps)36:14
- Whate Other Eloctrophiles ?39:17
- Aldol Condensation39:38
- Aldol Condensation39:39
- Aldol Mechanism41:26
- Aldol Mechanism: In Base, Deprotonate First41:27
- Aldol Mechanism45:28
- Mechanism for Loss of H₂O45:29
- Collapse of CTI and β-elimination Mechanism47:51
- Loss of H₂0 is not E2!48:39
- Aldol Summary49:53
- Aldol Summary49:54
- Base-Catalyzed Mechanism52:34
- Acid-Catalyzed Mechansim53:01
- Acid-Catalyzed Aldol Mechanism54:01
- First Step: Make Enol54:02
- Acid-Catalyzed Aldol Mechanism56:54
- Loss of H₂0 (β elimination)56:55
- Crossed/Mixed Aldol1:00:55
- Crossed/Mixed Aldol & Compound with α H's1:00:56
- Ketone vs. Aldehyde1:02:30
- Crossed/Mixed Aldol & Compound with α H's Continue1:03:10
- Crossed/Mixed Aldol1:05:21
- Mixed Aldol: control Using LDA1:05:22
- Crossed/Mixed Aldol Retrosynthesis1:08:53
- Example: Predic Aldol Starting Material (Aldol Retrosyntheiss)1:08:54
- Claisen Condensation1:12:54
- Claisen Condensation (Aldol on Esters)1:12:55
- Claisen Condensation1:19:52
- Example 1: Claisen Condensation1:19:53
- Claisen Condensation1:22:48
- Example 2: Claisen Condensation1:22:49
50m 57s
- Intro0:00
- Conjugate Additions0:06
- α, β-unsaturated Carbonyls0:07
- Conjugate Additions1:50
- '1,2-addition'1:51
- '1,-4-addition' or 'Conjugate Addition'2:24
- Conjugate Additions4:53
- Why can a Nu: Add to this Alkene?4:54
- Typical Alkene5:09
- α, β-unsaturated Alkene5:39
- Electrophilic Alkenes: Michael Acceptors6:35
- Other 'Electrophilic' Alkenes (Called 'Michael Acceptors)6:36
- 1,4-Addition of Cuprates (R2CuLi)8:29
- 1,4-Addition of Cuprates (R2CuLi)8:30
- 1,4-Addition of Cuprates (R2CuLi)11:23
- Use Cuprates in Synthesis11:24
- Preparation of Cuprates12:25
- Prepare Organocuprate From Organolithium12:26
- Cuprates Also Do SN2 with RX E+ (Not True for RMgX, RLi)13:06
- 1,4-Addition of Enolates: Michael Reaction13:50
- 1,4-Addition of Enolates: Michael Reaction13:51
- Mechanism15:57
- 1,4-Addition of Enolates: Michael Reaction18:47
- Example: 1,4-Addition of Enolates18:48
- 1,4-Addition of Enolates: Michael Reaction21:02
- Michael Reaction, Followed by Intramolecular Aldol21:03
- Mechanism of the Robinson Annulation24:26
- Mechanism of the Robinson Annulation24:27
- Enols and Enolates: Advanced Synthesis Topics31:10
- Stablized Enolates and the Decarboxylation Reaction31:11
- Mechanism: A Pericyclic Reaction32:08
- Enols and Enolates: Advanced Synthesis Topics33:32
- Example: Advance Synthesis33:33
- Enols and Enolates: Advanced Synthesis Topics36:10
- Common Reagents: Diethyl Malonate36:11
- Common Reagents: Ethyl Acetoacetate37:27
- Enols and Enolates: Advanced Synthesis Topics38:06
- Example: Transform38:07
- Advanced Synthesis Topics: Enamines41:52
- Enamines41:53
- Advanced Synthesis Topics: Enamines43:06
- Reaction with Ketone/Aldehyde43:07
- Example44:08
- Advanced Synthesis Topics: Enamines45:31
- Example: Use Enamines as Nu: (Like Enolate)45:32
- Advanced Synthesis Topics: Enamines47:56
- Example47:58
1h 59s
- Intro0:00
- Aromatic Compounds0:05
- Benzene0:06
- 3D Sketch1:33
- Features of Benzene4:41
- Features of Benzene4:42
- Aromatic Stability6:41
- Resonance Stabilization of Benzene6:42
- Cyclohexatriene7:24
- Benzene (Actual, Experimental)8:11
- Aromatic Stability9:03
- Energy Graph9:04
- Aromaticity Requirements9:55
- 1) Cyclic and Planar9:56
- 2) Contiguous p Orbitals10:49
- 3) Satisfy Huckel's Rule11:20
- Example: Benzene12:32
- Common Aromatic Compounds13:28
- Example: Pyridine13:29
- Common Aromatic Compounds16:25
- Example: Furan16:26
- Common Aromatic Compounds19:42
- Example: Thiophene19:43
- Example: Pyrrole20:18
- Common Aromatic Compounds21:09
- Cyclopentadienyl Anion21:10
- Cycloheptatrienyl Cation23:48
- Naphthalene26:04
- Determining Aromaticity27:28
- Example: Which of the Following are Aromatic?27:29
- Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory32:26
- What's So Special About '4n + 2' Electrons?32:27
- π bond & Overlapping p Orbitals32:53
- Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagrams36:56
- MO Diagram: Benzene36:58
- Drawing MO Diagrams44:26
- Example: 3-Membered Ring44:27
- Example: 4-Membered Ring46:04
- Drawing MO Diagrams47:51
- Example: 5-Membered Ring47:52
- Example: 8-Membered Ring49:32
- Aromaticity and Reactivity51:03
- Example: Which is More Acidic?51:04
- Aromaticity and Reactivity56:03
- Example: Which has More Basic Nitrogen, Pyrrole or Pyridine?56:04
1h 24m 4s
- Intro0:00
- Reactions of Benzene0:07
- N/R as Alkenes0:08
- Substitution Reactions0:50
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution1:24
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution1:25
- Mechanism Step 1: Addition of Electrophile2:08
- Mechanism Step 2: Loss of H+4:14
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Substituted Benzenes5:21
- Electron Donating Group5:22
- Electron Withdrawing Group8:02
- Halogen9:23
- Effects of Electron-Donating Groups (EDG)10:23
- Effects of Electron-Donating Groups (EDG)10:24
- What Effect Does EDG (OH) Have?11:40
- Reactivity13:03
- Regioselectivity14:07
- Regioselectivity: EDG is o/p Director14:57
- Prove It! Add E+ and Look at Possible Intermediates14:58
- Is OH Good or Bad?17:38
- Effects of Electron-Withdrawing Groups (EWG)20:20
- What Effect Does EWG Have?20:21
- Reactivity21:28
- Regioselectivity22:24
- Regioselectivity: EWG is a Meta Director23:23
- Prove It! Add E+ and Look at Competing Intermediates23:24
- Carbocation: Good or Bad?26:01
- Effects of Halogens on EAS28:33
- Inductive Withdrawal of e- Density vs. Resonance Donation28:34
- Summary of Substituent Effects on EAS32:33
- Electron Donating Group32:34
- Electron Withdrawing Group33:37
- Directing Power of Substituents34:35
- Directing Power of Substituents34:36
- Example36:41
- Electrophiles for Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution38:43
- Reaction: Halogenation38:44
- Electrophiles for Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution40:27
- Reaction: Nitration40:28
- Electrophiles for Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution41:45
- Reaction: Sulfonation41:46
- Electrophiles for Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution43:19
- Reaction: Friedel-Crafts Alkylation43:20
- Electrophiles for Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution45:43
- Reaction: Friedel-Crafts Acylation45:44
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Nitration46:52
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Nitration46:53
- Mechanism48:56
- Nitration of Aniline52:40
- Nitration of Aniline Part 152:41
- Nitration of Aniline Part 2: Why?54:12
- Nitration of Aniline56:10
- Workaround: Protect Amino Group as an Amide56:11
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Sulfonation58:16
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Sulfonation58:17
- Example: Transform59:25
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Friedel-Crafts Alkylation1:02:24
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Friedel-Crafts Alkylation1:02:25
- Example & Mechanism1:03:37
- Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Drawbacks1:05:48
- A) Can Over-React (Dialkylation)1:05:49
- Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Drawbacks1:08:21
- B) Carbocation Can Rearrange1:08:22
- Mechanism1:09:33
- Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Drawbacks1:13:35
- Want n-Propyl? Use Friedel-Crafts Acylation1:13:36
- Reducing Agents1:16:45
- Synthesis with Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution1:18:45
- Example: Transform1:18:46
- Synthesis with Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution1:20:59
- Example: Transform1:21:00
59m 10s
- Intro0:00
- Reagents for Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution0:07
- Reagents for Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution0:08
- Preparation of Diazonium Salt2:12
- Preparation of Diazonium Salt2:13
- Reagents for Sandmeyer Reactions4:14
- Reagents for Sandmeyer Reactions4:15
- Apply Diazonium Salt in Synthesis6:20
- Example: Transform6:21
- Apply Diazonium Salt in Synthesis9:14
- Example: Synthesize Following Target Molecule from Benzene or Toluene9:15
- Apply Diazonium Salt in Synthesis14:56
- Example: Transform14:57
- Reactions of Aromatic Substituents21:56
- A) Reduction Reactions21:57
- Reactions of Aromatic Substituents23:24
- B) Oxidations of Arenes23:25
- Benzylic [ox] Even Breaks C-C Bonds!25:05
- Benzylic Carbon Can't Be Quaternary25:55
- Reactions of Aromatic Substituents26:21
- Example26:22
- Review of Benzoic Acid Synthesis27:34
- Via Hydrolysis27:35
- Via Grignard28:20
- Reactions of Aromatic Substituents29:15
- C) Benzylic Halogenation29:16
- Radical Stabilities31:55
- N-bromosuccinimide (NBS)32:23
- Reactions of Aromatic Substituents33:08
- D) Benzylic Substitutions33:09
- Reactions of Aromatic Side Chains37:08
- Example: Transform37:09
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution43:13
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution43:14
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution47:08
- Example47:09
- Mechanism48:00
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution50:43
- Example50:44
- Nucleophilic Substitution: Benzyne Mechanism52:46
- Nucleophilic Substitution: Benzyne Mechanism52:47
- Nucleophilic Substitution: Benzyne Mechanism57:31
- Example: Predict Product57:32
1h 9m 12s
- Intro0:00
- Conjugated Dienes0:08
- Conjugated π Bonds0:09
- Diene Stability2:00
- Diene Stability: Cumulated2:01
- Diene Stability: Isolated2:37
- Diene Stability: Conjugated2:51
- Heat of Hydrogenation3:00
- Allylic Carbocations and Radicals5:15
- Allylic Carbocations and Radicals5:16
- Electrophilic Additions to Dienes7:00
- Alkenes7:01
- Unsaturated Ketone7:47
- Electrophilic Additions to Dienes8:28
- Conjugated Dienes8:29
- Electrophilic Additions to Dienes9:46
- Mechanism (2-Steps): Alkene9:47
- Electrophilic Additions to Dienes11:40
- Mechanism (2-Steps): Diene11:41
- 1,2 'Kinetic' Product13:08
- 1,4 'Thermodynamic' Product14:47
- E vs. POR Diagram15:50
- E vs. POR Diagram15:51
- Kinetic vs. Thermodynamic Control21:56
- Kinetic vs. Thermodynamic Control21:57
- How? Reaction is Reversible!23:51
- 1,2 (Less Stable product)23:52
- 1,4 (More Stable Product)25:16
- Diels Alder Reaction26:34
- Diels Alder Reaction26:35
- Dienophiles (E+)29:23
- Dienophiles (E+)29:24
- Alkyne Diels-Alder Example30:48
- Example: Alkyne Diels-Alder30:49
- Diels-Alder Reaction: Dienes (Nu:)32:22
- Diels-Alder ReactionL Dienes (Nu:)32:23
- Diels-Alder Reaction: Dienes33:51
- Dienes Must Have 's-cis' Conformation33:52
- Example35:25
- Diels-Alder Reaction with Cyclic Dienes36:08
- Cyclic Dienes are Great for Diels-Alder Reaction36:09
- Cyclopentadiene37:10
- Diels-Alder Reaction: Bicyclic Products40:50
- Endo vs. Exo Terminology: Norbornane & Bicyclo Heptane40:51
- Example: Bicyclo Heptane42:29
- Diels-Alder Reaction with Cyclic Dienes44:15
- Example44:16
- Stereochemistry of the Diels-Alder Reaction47:39
- Stereochemistry of the Diels-Alder Reaction47:40
- Example48:08
- Stereochemistry of the Diels-Alder Reaction50:21
- Example50:22
- Regiochemistry of the Diels-Alder Reaction52:42
- Rule: 1,2-Product Preferred Over 1,3-Product52:43
- Regiochemistry of the Diels-Alder Reaction54:18
- Rule: 1,4-Product Preferred Over 1,3-Product54:19
- Regiochemistry of the Diels-Alder Reaction55:02
- Why 1,2-Product or 1,4-Product Favored?55:03
- Example56:11
- Diels-Alder Reaction58:06
- Example: Predict58:07
- Diels-Alder Reaction1:01:27
- Explain Why No Diels-Alder Reaction Takes Place in This Case1:01:28
- Diels-Alder Reaction1:03:09
- Example: Predict1:03:10
- Diels-Alder Reaction: Synthesis Problem1:05:39
- Diels-Alder Reaction: Synthesis Problem1:05:40
1h 21m 31s
- Intro0:00
- Pericyclic Reactions0:05
- Pericyclic Reactions0:06
- Electrocyclic Reactions1:19
- Electrocyclic Reactions1:20
- Electrocyclic Reactions3:13
- Stereoselectivity3:14
- Electrocyclic Reactions8:10
- Example: Predict8:11
- Sigmatropic Rearrangements12:29
- Sigmatropic Rearrangements12:30
- Cope Rearrangement14:44
- Sigmatropic Rearrangements16:44
- Claisen Rearrangement 116:45
- Claisen Rearrangement 217:46
- Cycloaddition Reactions19:22
- Diels-Alder19:23
- 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition20:32
- Cycloaddition Reactions: Stereochemistry21:58
- Cycloaddition Reactions: Stereochemistry21:59
- Cycloaddition Reactions: Heat or Light?26:00
- 4+2 Cycloadditions26:01
- 2+2 Cycloadditions27:23
- Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of Chemical Reactions29:26
- Example 1: Molecular Orbital Theory of Bonding29:27
- Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of Chemical Reactions31:59
- Example 2: Molecular Orbital Theory of Bonding32:00
- Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of Chemical Reactions33:33
- MO Theory of Aromaticity, Huckel's Rule33:34
- Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of Chemical Reactions36:43
- Review: Molecular Orbital Theory of Conjugated Systems36:44
- Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of Chemical Reactions44:56
- Review: Molecular Orbital Theory of Conjugated Systems44:57
- Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of Chemical Reactions46:54
- Review: Molecular Orbital Theory of Conjugated Systems46:55
- Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of Chemical Reactions48:36
- Frontier Molecular Orbitals are Involved in Reactions48:37
- Examples50:20
- MO Theory of Pericyclic Reactions: The Woodward-Hoffmann Rules51:51
- Heat-promoted Pericyclic Reactions and Light-promoted Pericyclic Reactions51:52
- MO Theory of Pericyclic Reactions: The Woodward-Hoffmann Rules53:42
- Why is a [4+2] Cycloaddition Thermally Allowed While the [2+2] is Not?53:43
- MO Theory of Pericyclic Reactions: The Woodward-Hoffmann Rules56:51
- Why is a [2+2] Cycloaddition Photochemically Allowed?56:52
- Pericyclic Reaction Example I59:16
- Pericyclic Reaction Example I59:17
- Pericyclic Reaction Example II1:07:40
- Pericyclic Reaction Example II1:07:41
- Pericyclic Reaction Example III: Vitamin D - The Sunshine Vitamin1:14:22
- Pericyclic Reaction Example III: Vitamin D - The Sunshine Vitamin1:14:23
34m 58s
- Intro0:00
- Amines: Properties and Reactivity0:04
- Compare Amines to Alcohols0:05
- Amines: Lower Boiling Point than ROH0:55
- 1) RNH₂ Has Lower Boiling Point than ROH0:56
- Amines: Better Nu: Than ROH2:22
- 2) RNH₂ is a Better Nucleophile than ROH Example 12:23
- RNH₂ is a Better Nucleophile than ROH Example 23:08
- Amines: Better Nu: than ROH3:47
- Example3:48
- Amines are Good Bases5:41
- 3) RNH₂ is a Good Base5:42
- Amines are Good Bases7:06
- Example 17:07
- Example 2: Amino Acid8:27
- Alkyl vs. Aryl Amines9:56
- Example: Which is Strongest Base?9:57
- Alkyl vs. Aryl Amines14:55
- Verify by Comparing Conjugate Acids14:56
- Reaction of Amines17:42
- Reaction with Ketone/Aldehyde: 1° Amine (RNH₂)17:43
- Reaction of Amines18:48
- Reaction with Ketone/Aldehyde: 2° Amine (R2NH)18:49
- Use of Enamine: Synthetic Equivalent of Enolate20:08
- Use of Enamine: Synthetic Equivalent of Enolate20:09
- Reaction of Amines24:10
- Hofmann Elimination24:11
- Hofmann Elimination26:16
- Kinetic Product26:17
- Structure Analysis Using Hofmann Elimination28:22
- Structure Analysis Using Hofmann Elimination28:23
- Biological Activity of Amines30:30
- Adrenaline31:07
- Mescaline (Peyote Alkaloid)31:22
- Amino Acids, Amide, and Protein32:14
- Biological Activity of Amines32:50
- Morphine (Opium Alkaloid)32:51
- Epibatidine (Poison Dart Frog)33:28
- Nicotine33:48
- Choline (Nerve Impulse)34:03
1h 53m 20s
- Intro0:00
- Carbohydrates1:11
- D-glucose Overview1:12
- D-glucose: Cyclic Form (6-membered ring)4:31
- Cyclic Forms of Glucose: 6-membered Ring8:24
- α-D-glucopyranose & β-D-glucopyranose8:25
- Formation of a 5-Membered Ring11:05
- D-glucose: Formation of a 5-Membered Ring11:06
- Cyclic Forms of Glucose: 5-membered Ring12:37
- α-D-glucofuranose & β-D-glucofuranose12:38
- Carbohydrate Mechanism14:03
- Carbohydrate Mechanism14:04
- Reactions of Glucose: Acetal Formation21:35
- Acetal Formation: Methyl-α-D-glucoside21:36
- Hemiacetal to Acetal: Overview24:58
- Mechanism for Formation of Glycosidic Bond25:51
- Hemiacetal to Acetal: Mechanism25:52
- Formation of Disaccharides29:34
- Formation of Disaccharides29:35
- Some Polysaccharides: Starch31:33
- Amylose & Amylopectin31:34
- Starch: α-1,4-glycosidic Bonds32:22
- Properties of Starch Molecule33:21
- Some Polysaccharides: Cellulose33:59
- Cellulose: β-1,4-glycosidic bonds34:00
- Properties of Cellulose34:59
- Other Sugar-Containing Biomolecules35:50
- Ribonucleoside (RNA)35:51
- Deoxyribonucleoside (DMA)36:59
- Amino Acids & Proteins37:32
- α-amino Acids: Structure & Stereochemistry37:33
- Making a Protein (Condensation)42:46
- Making a Protein (Condensation)42:47
- Peptide Bond is Planar (Amide Resonance)44:55
- Peptide Bond is Planar (Amide Resonance)44:56
- Protein Functions47:49
- Muscle, Skin, Bones, Hair Nails47:50
- Enzymes49:10
- Antibodies49:44
- Hormones, Hemoglobin49:58
- Gene Regulation50:20
- Various Amino Acid Side Chains50:51
- Nonpolar50:52
- Polar51:15
- Acidic51:24
- Basic51:55
- Amino Acid Table52:22
- Amino Acid Table52:23
- Isoelectric Point (pI)53:43
- Isoelectric Point (pI) of Glycine53:44
- Isoelectric Point (pI) of Glycine: pH 1156:42
- Isoelectric Point (pI) of Glycine: pH 157:20
- Isoelectric Point (pI), cont.58:05
- Asparatic Acid58:06
- Histidine1:00:28
- Isoelectric Point (pI), cont.1:02:54
- Example: What is the Net Charge of This Tetrapeptide at pH 6.0?1:02:55
- Nucleic Acids: Ribonucleosides1:10:32
- Nucleic Acids: Ribonucleosides1:10:33
- Nucleic Acids: Ribonucleotides1:11:48
- Ribonucleotides: 5' Phosphorylated Ribonucleosides1:11:49
- Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Structure1:12:35
- Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Structure1:12:36
- Nucleic Acids: Deoxyribonucleosides1:14:08
- Nucleic Acids: Deoxyribonucleosides1:14:09
- Deoxythymidine (T)1:14:36
- Nucleic Acids: Base-Pairing1:15:17
- Nucleic Acids: Base-Pairing1:15:18
- Double-Stranded Structure of DNA1:18:16
- Double-Stranded Structure of DNA1:18:17
- Model of DNA1:19:40
- Model of DNA1:19:41
- Space-Filling Model of DNA1:20:46
- Space-Filling Model of DNA1:20:47
- Function of RNA and DNA1:23:06
- DNA & Transcription1:23:07
- RNA & Translation1:24:22
- Genetic Code1:25:09
- Genetic Code1:25:10
- Lipids/Fats/Triglycerides1:27:10
- Structure of Glycerol1:27:43
- Saturated & Unsaturated Fatty Acids1:27:51
- Triglyceride1:28:43
- Unsaturated Fats: Lower Melting Points (Liquids/Oils)1:29:15
- Saturated Fat1:29:16
- Unsaturated Fat1:30:10
- Partial Hydrogenation1:32:05
- Saponification of Fats1:35:11
- Saponification of Fats1:35:12
- History of Soap1:36:50
- Carboxylate Salts form Micelles in Water1:41:02
- Carboxylate Salts form Micelles in Water1:41:03
- Cleaning Power of Micelles1:42:21
- Cleaning Power of Micelles1:42:22
- 3-D Image of a Micelle1:42:58
- 3-D Image of a Micelle1:42:59
- Synthesis of Biodiesel1:44:04
- Synthesis of Biodiesel1:44:05
- Phosphoglycerides1:47:54
- Phosphoglycerides1:47:55
- Cell Membranes Contain Lipid Bilayers1:48:41
- Cell Membranes Contain Lipid Bilayers1:48:42
- Bilayer Acts as Barrier to Movement In/Out of Cell1:50:24
- Bilayer Acts as Barrier to Movement In/Out of Cell1:50:25
- Organic Chemistry Meets Biology… Biochemistry!1:51:12
- Organic Chemistry Meets Biology… Biochemistry!1:51:13
45m 47s
- Intro0:00
- Polymers0:05
- Monomer to Polymer: Vinyl Chloride to Polyvinyl Chloride0:06
- Polymer Properties1:32
- Polymer Properties1:33
- Natural Polymers: Rubber2:30
- Vulcanization2:31
- Natural Polymers: Polysaccharides4:55
- Example: Starch4:56
- Example: Cellulose5:45
- Natural Polymers: Proteins6:07
- Example: Keratin6:08
- DNA Strands7:15
- DNA Strands7:16
- Synthetic Polymers8:30
- Ethylene & Polyethylene: Lightweight Insulator & Airtight Plastic8:31
- Synthetic Organic Polymers12:22
- Polyethylene12:28
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)12:54
- Polystyrene13:28
- Polyamide14:34
- Polymethyl Methacrylate14:57
- Kevlar15:25
- Synthetic Material Examples16:30
- How are Polymers Made?21:00
- Chain-growth Polymers Additions to Alkenes can be Radical, Cationic or Anionic21:01
- Chain Branching22:34
- Chain Branching22:35
- Special Reaction Conditions Prevent Branching24:28
- Ziegler-Natta Catalyst24:29
- Chain-Growth by Cationic Polymerization27:35
- Chain-Growth by Cationic Polymerization27:36
- Chain-Growth by Anionic Polymerization29:35
- Chain-Growth by Anionic Polymerization29:36
- Step-Growth Polymerization: Polyamides32:16
- Step-Growth Polymerization: Polyamides32:17
- Step-Growth Polymerization: Polyesters34:23
- Step-Growth Polymerization: Polyesters34:24
- Step-Growth Polymerization: Polycarbonates35:56
- Step-Growth Polymerization: Polycarbonates35:57
- Step-Growth Polymerization: Polyurethanes37:18
- Step-Growth Polymerization: Polyurethanes37:19
- Modifying Polymer Properties39:35
- Glass Transition Temperature40:04
- Crosslinking40:42
- Copolymers40:58
- Additives: Stabilizers42:08
- Additives: Flame Retardants43:03
- Additives: Plasticizers43:41
- Additives: Colorants44:54
2h 20m 24s
- Intro0:00
- Organic Synthesis Strategies0:15
- Goal0:16
- Strategy0:29
- Example of a RetroSynthesis1:30
- Finding Starting Materials for Target Molecule1:31
- Synthesis Using Starting Materials4:56
- Synthesis of Alcohols by Functional Group Interconversion (FGI)6:00
- Synthesis of Alcohols by Functional Group Interconversion Overview6:01
- Alcohols by Reduction7:43
- Ketone to Alcohols7:45
- Aldehyde to Alcohols8:26
- Carboxylic Acid Derivative to Alcohols8:36
- Alcohols by Hydration of Alkenes9:28
- Hydration of Alkenes Using H₃O⁺9:29
- Oxymercuration-Demercuration10:35
- Hydroboration Oxidation11:02
- Alcohols by Substitution11:42
- Primary Alkyl Halide to Alcohols Using NaOH11:43
- Secondary Alkyl Halide to Alcohols Using Sodium Acetate13:07
- Tertiary Alkyl Halide to Alcohols Using H₂O15:08
- Synthesis of Alcohols by Forming a New C-C Bond15:47
- Recall: Alcohol & RMgBr15:48
- Retrosynthesis17:28
- Other Alcohol Disconnections19:46
- 19:47
- Synthesis Using PhMGgBr: Example 223:05
- Synthesis of Alkyl Halides26:06
- Synthesis of Alkyl Halides Overview26:07
- Synthesis of Alkyl Halides by Free Radical Halogenation27:04
- Synthesis of Alkyl Halides by Free Radical Halogenation27:05
- Synthesis of Alkyl Halides by Substitution29:06
- Alcohol to Alkyl Halides Using HBr or HCl29:07
- Alcohol to Alkyl Halides Using SOCl₂30:57
- Alcohol to Alkyl Halides Using PBr₃ and Using P, I₂31:03
- Synthesis of Alkyl Halides by Addition32:02
- Alkene to Alkyl Halides Using HBr32:03
- Alkene to Alkyl Halides Using HBr & ROOR (Peroxides)32:35
- Example: Synthesis of Alkyl Halide34:18
- Example: Synthesis of Alkyl Halide34:19
- Synthesis of Ethers39:25
- Synthesis of Ethers39:26
- Example: Synthesis of an Ether41:12
- Synthesize TBME (t-butyl methyl ether) from Alcohol Starting Materials41:13
- Synthesis of Amines46:05
- Synthesis of Amines46:06
- Gabriel Synthesis of Amines47:57
- Gabriel Synthesis of Amines47:58
- Amines by SN2 with Azide Nu:49:50
- Amines by SN2 with Azide Nu:49:51
- Amines by SN2 with Cyanide Nu:50:31
- Amines by SN2 with Cyanide Nu:50:32
- Amines by Reduction of Amides51:30
- Amines by Reduction of Amides51:31
- Reductive Amination of Ketones/Aldehydes52:42
- Reductive Amination of Ketones/Aldehydes52:43
- Example : Synthesis of an Amine53:47
- Example 1: Synthesis of an Amine53:48
- Example 2: Synthesis of an Amine56:16
- Synthesis of Alkenes58:20
- Synthesis of Alkenes Overview58:21
- Synthesis of Alkenes by Elimination59:04
- Synthesis of Alkenes by Elimination Using NaOH & Heat59:05
- Synthesis of Alkenes by Elimination Using H₂SO₄ & Heat59:57
- Synthesis of Alkenes by Reduction1:02:05
- Alkyne to Cis Alkene1:02:06
- Alkyne to Trans Alkene1:02:56
- Synthesis of Alkenes by Wittig Reaction1:03:46
- Synthesis of Alkenes by Wittig Reaction1:03:47
- Retrosynthesis of an Alkene1:05:35
- Example: Synthesis of an Alkene1:06:57
- Example: Synthesis of an Alkene1:06:58
- Making a Wittig Reagent1:10:31
- Synthesis of Alkynes1:13:09
- Synthesis of Alkynes1:13:10
- Synthesis of Alkynes by Elimination (FGI)1:13:42
- First Step: Bromination of Alkene1:13:43
- Second Step: KOH Heat1:14:22
- Synthesis of Alkynes by Alkylation1:15:02
- Synthesis of Alkynes by Alkylation1:15:03
- Retrosynthesis of an Alkyne1:16:18
- Example: Synthesis of an Alkyne1:17:40
- Example: Synthesis of an Alkyne1:17:41
- Synthesis of Alkanes1:20:52
- Synthesis of Alkanes1:20:53
- Synthesis of Aldehydes & Ketones1:21:38
- Oxidation of Alcohol Using PCC or Swern1:21:39
- Oxidation of Alkene Using 1) O₃, 2)Zn1:22:42
- Reduction of Acid Chloride & Nitrile Using DiBAL-H1:23:25
- Hydration of Alkynes1:24:55
- Synthesis of Ketones by Acyl Substitution1:26:12
- Reaction with R'₂CuLi1:26:13
- Reaction with R'MgBr1:27:13
- Synthesis of Aldehydes & Ketones by α-Alkylation1:28:00
- Synthesis of Aldehydes & Ketones by α-Alkylation1:28:01
- Retrosynthesis of a Ketone1:30:10
- Acetoacetate Ester Synthesis of Ketones1:31:05
- Acetoacetate Ester Synthesis of Ketones: Step 11:31:06
- Acetoacetate Ester Synthesis of Ketones: Step 21:32:13
- Acetoacetate Ester Synthesis of Ketones: Step 31:32:50
- Example: Synthesis of a Ketone1:34:11
- Example: Synthesis of a Ketone1:34:12
- Synthesis of Carboxylic Acids1:37:15
- Synthesis of Carboxylic Acids1:37:16
- Example: Synthesis of a Carboxylic Acid1:37:59
- Example: Synthesis of a Carboxylic Acid (Option 1)1:38:00
- Example: Synthesis of a Carboxylic Acid (Option 2)1:40:51
- Malonic Ester Synthesis of Carboxylic Acid1:42:34
- Malonic Ester Synthesis of Carboxylic Acid: Step 11:42:35
- Malonic Ester Synthesis of Carboxylic Acid: Step 21:43:36
- Malonic Ester Synthesis of Carboxylic Acid: Step 31:44:01
- Example: Synthesis of a Carboxylic Acid1:44:53
- Example: Synthesis of a Carboxylic Acid1:44:54
- Synthesis of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives1:48:05
- Synthesis of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives1:48:06
- Alternate Ester Synthesis1:48:58
- Using Fischer Esterification1:48:59
- Using SN2 Reaction1:50:18
- Using Diazomethane1:50:56
- Using 1) LDA, 2) R'-X1:52:15
- Practice: Synthesis of an Alkyl Chloride1:53:11
- Practice: Synthesis of an Alkyl Chloride1:53:12
- Patterns of Functional Groups in Target Molecules1:59:53
- Recall: Aldol Reaction1:59:54
- β-hydroxy Ketone Target Molecule2:01:12
- α,β-unsaturated Ketone Target Molecule2:02:20
- Patterns of Functional Groups in Target Molecules2:03:15
- Recall: Michael Reaction2:03:16
- Retrosynthesis: 1,5-dicarbonyl Target Molecule2:04:07
- Patterns of Functional Groups in Target Molecules2:06:38
- Recall: Claisen Condensation2:06:39
- Retrosynthesis: β-ketoester Target Molecule2:07:30
- 2-Group Target Molecule Summary2:09:03
- 2-Group Target Molecule Summary2:09:04
- Example: Synthesis of Epoxy Ketone2:11:19
- Synthesize the Following Target Molecule from Cyclohexanone: Part 1 - Retrosynthesis2:11:20
- Synthesize the Following Target Molecule from Cyclohexanone: Part 2 - Synthesis2:14:10
- Example: Synthesis of a Diketone2:16:57
- Synthesis of a Diketone: Step 1 - Retrosynthesis2:16:58
- Synthesis of a Diketone: Step 2 - Synthesis2:18:51
46m 46s
- Intro0:00
- Organic Analysis: Classical Methods0:17
- Classical Methods for Identifying Chemicals0:18
- Organic Analysis: Classical Methods2:21
- When is Structure Identification Needed?2:22
- Organic Analysis: Classical Methods6:17
- Classical Methods of Structure Identification: Physical Appearance6:18
- Classical Methods of Structure Identification: Physical Constants6:42
- Organic Analysis: Classical Methods7:37
- Classical Methods of Structure Identification: Solubility Tests - Water7:38
- Organic Analysis: Classical Methods10:51
- Classical Methods of Structure Identification: Solubility Tests - 5% aq. HCl Basic FG (Amines)10:52
- Organic Analysis: Classical Methods11:50
- Classical Methods of Structure Identification: Solubility Tests - 5% aq. NaOH Acidic FG (Carboxylic Acids, Phenols)11:51
- Organic Analysis: Classical Methods13:28
- Classical Methods of Structure Identification: Solubility Tests - 5% aq. NaHCO3 Strongly Acidic FG (Carboxylic Acids)13:29
- Organic Analysis: Classical Methods15:35
- Classical Methods of Structure Identification: Solubility Tests - Insoluble in All of the Above15:36
- Organic Analysis: Classical Methods16:49
- Classical Methods of Structure Identification: Idoform Test for Methyl Ketones16:50
- Organic Analysis: Classical Methods22:02
- Classical Methods of Structure Identification: Tollens' Test or Fehling's Solution for Aldehydes22:03
- Organic Analysis: Classical Methods25:01
- Useful Application of Classical Methods: Glucose Oxidase on Glucose Test Strips25:02
- Organic Analysis: Classical Methods26:26
- Classical Methods of Structure Identification: Starch-iodide Test26:27
- Organic Analysis: Classical Methods28:22
- Classical Methods of Structure Identification: Lucas Reagent to Determine Primary/Secondary/Tertiary Alcohol28:23
- Organic Analysis: Classical Methods31:35
- Classical Methods of Structure Identification: Silver Nitrate Test for Alkyl Halides31:36
- Organic Analysis: Classical Methods33:23
- Preparation of Derivatives33:24
- Organic Analysis: Modern Methods36:55
- Modern Methods of Chemical Characterization36:56
- Organic Analysis: Modern Methods40:36
- Checklist for Manuscripts Submitted to the ACS Journal Organic Letters40:37
- Organic Analysis: Modern Methods42:39
- Checklist for Manuscripts Submitted to the ACS Journal Organic Letters42:40
1h 2m 52s
- Intro0:00
- Chirality & Optical Activity0:32
- Levorotatory & Dextrorotatory0:33
- Example: Optically Active?2:22
- Example: Optically Active?2:23
- Measurement of Specific Rotation, [α]5:09
- Measurement of Specific Rotation, [α]5:10
- Example: Calculation of Specific Rotation8:56
- Example: Calculation of Specific Rotation8:57
- Variability of Specific Rotation, [α]12:52
- Variability of Specific Rotation, [α]12:53
- Other Measures of Optical Activity: ORD and CD15:04
- Optical Rotary Dispersion (ORD)15:05
- Circular Dischroism (CD)18:32
- Circular Dischroism (CD)18:33
- Mixtures of Enantiomers20:16
- Racemic Mixtures20:17
- Unequal Mixtures of Enantiomers21:36
- 100% ee22:48
- 0% ee23:34
- Example: Definition of ee?24:00
- Example: Definition of ee?24:01
- Analysis of Optical Purity: [α]27:47
- [α] Measurement Can Be Used for Known Compounds27:48
- Analysis of Optical Purity: [α]34:30
- NMR Methods Using a Chiral Derivatizing Agent (CDA): Mosher's Reagent34:31
- Analysis of Optical Purity: [α]40:01
- NMR Methods Using a Chiral Derivatizing Agent (CDA): CDA Salt Formation40:02
- Analysis of Optical Purity: Chromatography42:46
- Chiral Chromatography42:47
- Stereochemistry Analysis by NMR: J Values (Coupling Constant)51:28
- NMR Methods for Structure Determination51:29
- Stereochemistry Analysis by NRM: NOE57:00
- NOE - Nuclear Overhauser Effect ( 2D Versions: NOESY or ROESY)57:01
1h 4m
- Intro0:00
- Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy0:09
- Introduction to Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy0:10
- Intensity of Absorption Is Proportional to Change in Dipole3:08
- IR Spectrum of an Alkane6:08
- Pentane6:09
- IR Spectrum of an Alkene13:12
- 1-Pentene13:13
- IR Spectrum of an Alkyne15:49
- 1-Pentyne15:50
- IR Spectrum of an Aromatic Compound18:02
- Methylbenzene18:24
- IR of Substituted Aromatic Compounds24:04
- IR of Substituted Aromatic Compounds24:05
- IR Spectrum of 1,2-Disubstituted Aromatic25:30
- 1,2-dimethylbenzene25:31
- IR Spectrum of 1,3-Disubstituted Aromatic27:15
- 1,3-dimethylbenzene27:16
- IR Spectrum of 1,4-Disubstituted Aromatic28:41
- 1,4-dimethylbenzene28:42
- IR Spectrum of an Alcohol29:34
- 1-pentanol29:35
- IR Spectrum of an Amine32:39
- 1-butanamine32:40
- IR Spectrum of a 2° Amine34:50
- Diethylamine34:51
- IR Spectrum of a 3° Amine35:47
- Triethylamine35:48
- IR Spectrum of a Ketone36:41
- 2-butanone36:42
- IR Spectrum of an Aldehyde40:10
- Pentanal40:11
- IR Spectrum of an Ester42:38
- Butyl Propanoate42:39
- IR Spectrum of a Carboxylic Acid44:26
- Butanoic Acid44:27
- Sample IR Correlation Chart47:36
- Sample IR Correlation Chart: Wavenumber and Functional Group47:37
- Predicting IR Spectra: Sample Structures52:06
- Example 152:07
- Example 253:29
- Example 354:40
- Example 457:08
- Example 558:31
- Example 659:07
- Example 71:00:52
- Example 81:02:20
48m 34s
- Intro0:00
- Interpretation of IR Spectra: a Basic Approach0:05
- Interpretation of IR Spectra: a Basic Approach0:06
- Other Peaks to Look for3:39
- Examples5:17
- Example 15:18
- Example 29:09
- Example 311:52
- Example 414:03
- Example 516:31
- Example 619:31
- Example 722:32
- Example 824:39
- IR Problems Part 128:11
- IR Problem 128:12
- IR Problem 231:14
- IR Problem 332:59
- IR Problem 434:23
- IR Problem 535:49
- IR Problem 638:20
- IR Problems Part 242:36
- IR Problem 742:37
- IR Problem 844:02
- IR Problem 945:07
- IR Problems1046:10
1h 32m 14s
- Intro0:00
- Purpose of NMR0:14
- Purpose of NMR0:15
- How NMR Works2:17
- How NMR Works2:18
- Information Obtained From a ¹H NMR Spectrum5:51
- No. of Signals, Integration, Chemical Shifts, and Splitting Patterns5:52
- Number of Signals in NMR (Chemical Equivalence)7:52
- Example 1: How Many Signals in ¹H NMR?7:53
- Example 2: How Many Signals in ¹H NMR?9:36
- Example 3: How Many Signals in ¹H NMR?12:15
- Example 4: How Many Signals in ¹H NMR?13:47
- Example 5: How Many Signals in ¹H NMR?16:12
- Size of Signals in NMR (Peak Area or Integration)21:23
- Size of Signals in NMR (Peak Area or Integration)21:24
- Using Integral Trails25:15
- Example 1: C₈H₁₈O25:16
- Example 2: C₃H₈O27:17
- Example 3: C₇H₈28:21
- Location of NMR Signal (Chemical Shift)29:05
- Location of NMR Signal (Chemical Shift)29:06
- ¹H NMR Chemical Shifts33:20
- ¹H NMR Chemical Shifts33:21
- ¹H NMR Chemical Shifts (Protons on Carbon)37:03
- ¹H NMR Chemical Shifts (Protons on Carbon)37:04
- Chemical Shifts of H's on N or O39:01
- Chemical Shifts of H's on N or O39:02
- Estimating Chemical Shifts41:13
- Example 1: Estimating Chemical Shifts41:14
- Example 2: Estimating Chemical Shifts43:22
- Functional Group Effects are Additive45:28
- Calculating Chemical Shifts47:38
- Methylene Calculation47:39
- Methine Calculation48:20
- Protons on sp³ Carbons: Chemical Shift Calculation Table48:50
- Example: Estimate the Chemical Shift of the Selected H50:29
- Effects of Resonance on Chemical Shifts53:11
- Example 1: Effects of Resonance on Chemical Shifts53:12
- Example 2: Effects of Resonance on Chemical Shifts55:09
- Example 3: Effects of Resonance on Chemical Shifts57:08
- Shape of NMR Signal (Splitting Patterns)59:17
- Shape of NMR Signal (Splitting Patterns)59:18
- Understanding Splitting Patterns: The 'n+1 Rule'1:01:24
- Understanding Splitting Patterns: The 'n+1 Rule'1:01:25
- Explanation of n+1 Rule1:02:42
- Explanation of n+1 Rule: One Neighbor1:02:43
- Explanation of n+1 Rule: Two Neighbors1:06:23
- Summary of Splitting Patterns1:06:24
- Summary of Splitting Patterns1:10:45
- Predicting ¹H NMR Spectra1:10:46
- Example 1: Predicting ¹H NMR Spectra1:13:30
- Example 2: Predicting ¹H NMR Spectra1:19:07
- Example 3: Predicting ¹H NMR Spectra1:23:50
- Example 4: Predicting ¹H NMR Spectra1:29:27
2h 3m 48s
- Intro0:00
- ¹H NMR Problem-Solving Strategies0:18
- Step 1: Analyze IR Spectrum (If Provided)0:19
- Step 2: Analyze Molecular Formula (If Provided)2:06
- Step 3: Draw Pieces of Molecule3:49
- Step 4: Confirm Pieces6:30
- Step 5: Put the Pieces Together!7:23
- Step 6: Check Your Answer!8:21
- Examples9:17
- Example 1: Determine the Structure of a C₉H₁₀O₂ Compound with the Following ¹H NMR Data9:18
- Example 2: Determine the Structure of a C₉H₁₀O₂ Compound with the Following ¹H NMR Data17:27
- ¹H NMR Practice20:57
- ¹H NMR Practice 1: C₁₀H₁₄20:58
- ¹H NMR Practice 2: C₄H₈O₂29:50
- ¹H NMR Practice 3: C₆H₁₂O₃39:19
- ¹H NMR Practice 4: C₈H₁₈50:19
- More About Coupling Constants (J Values)57:11
- Vicinal (3-bond) and Geminal (2-bond)57:12
- Cyclohexane (ax-ax) and Cyclohexane (ax-eq) or (eq-eq)59:50
- Geminal (Alkene), Cis (Alkene), and Trans (Alkene)1:02:40
- Allylic (4-bond) and W-coupling (4-bond) (Rigid Structures Only)1:04:05
- ¹H NMR Advanced Splitting Patterns1:05:39
- Example 1: ¹H NMR Advanced Splitting Patterns1:05:40
- Example 2: ¹H NMR Advanced Splitting Patterns1:10:01
- Example 3: ¹H NMR Advanced Splitting Patterns1:13:45
- ¹H NMR Practice1:22:53
- ¹H NMR Practice 5: C₁₁H₁₇N1:22:54
- ¹H NMR Practice 6: C₉H₁₀O1:34:04
- ¹³C NMR Spectroscopy1:44:49
- ¹³C NMR Spectroscopy1:44:50
- ¹³C NMR Chemical Shifts1:47:24
- ¹³C NMR Chemical Shifts Part 11:47:25
- ¹³C NMR Chemical Shifts Part 21:48:59
- ¹³C NMR Practice1:50:16
- ¹³C NMR Practice 11:50:17
- ¹³C NMR Practice 21:58:30
23m 10s
- Intro0:00
- C-13 DEPT NMR Spectoscopy0:13
- Overview0:14
- C-13 DEPT NMR Spectoscopy, Cont.3:31
- Match C-13 Peaks to Carbons on Structure3:32
- C-13 DEPT NMR Spectoscopy, Cont.8:46
- Predict the DEPT-90 and DEPT-135 Spectra for the Given Compound8:47
- C-13 DEPT NMR Spectoscopy, Cont.12:30
- Predict the DEPT-90 and DEPT-135 Spectra for the Given Compound12:31
- C-13 DEPT NMR Spectoscopy, Cont.17:19
- Determine the Structure of an Unknown Compound using IR Spectrum and C-13 DEPT NMR17:20
33m 39s
- Intro0:00
- Two-Dimensional NMR Techniques: COSY0:14
- How Do We Determine Which Protons are Related in the NMR?0:15
- Two-Dimensional NMR Techniques: COSY1:48
- COSY Spectra1:49
- Two-Dimensional NMR Techniques: COSY7:00
- COSY Correlation7:01
- Two-Dimensional NMR Techniques: COSY8:55
- Complete the COSY NMR Spectrum for the Given Compoun8:56
- NMR Practice Problem15:40
- Provide a Structure for the Unknown Compound with the H NMR and COSY Spectra Shown15:41
15m 5s
- Intro0:00
- HETCOR0:15
- Heteronuclear Correlation Spectroscopy0:16
- HETCOR2:04
- HETCOR Example2:05
- HMBC11:07
- Heteronuclear Multiple Bond Correlation11:08
- HMBC13:14
- HMB Example13:15
1h 28m 35s
- Intro0:00
- Introduction to Mass Spectrometry0:37
- Uses of Mass Spectrometry: Molecular Mass0:38
- Uses of Mass Spectrometry: Molecular Formula1:04
- Uses of Mass Spectrometry: Structural Information1:21
- Uses of Mass Spectrometry: In Conjunction with Gas Chromatography2:03
- Obtaining a Mass Spectrum2:59
- Obtaining a Mass Spectrum3:00
- The Components of a Mass Spectrum6:44
- The Components of a Mass Spectrum6:45
- What is the Mass of a Single Molecule12:13
- Example: CH₄12:14
- Example: ¹³CH₄12:51
- What Ratio is Expected for the Molecular Ion Peaks of C₂H₆?14:20
- Other Isotopes of High Abundance16:30
- Example: Cl Atoms16:31
- Example: Br Atoms18:33
- Mass Spectrometry of Chloroethane19:22
- Mass Spectrometry of Bromobutane21:23
- Isotopic Abundance can be Calculated22:48
- What Ratios are Expected for the Molecular Ion Peaks of CH₂Br₂?22:49
- Determining Molecular Formula from High-resolution Mass Spectrometry26:53
- Exact Masses of Various Elements26:54
- Fragmentation of various Functional Groups28:42
- What is More Stable, a Carbocation C⁺ or a Radical R?28:43
- Fragmentation is More Likely If It Gives Relatively Stable Carbocations and Radicals31:37
- Mass Spectra of Alkanes33:15
- Example: Hexane33:16
- Fragmentation Method 134:19
- Fragmentation Method 235:46
- Fragmentation Method 336:15
- Mass of Common Fragments37:07
- Mass of Common Fragments37:08
- Mass Spectra of Alkanes39:28
- Mass Spectra of Alkanes39:29
- What are the Peaks at m/z 15 and 71 So Small?41:01
- Branched Alkanes43:12
- Explain Why the Base Peak of 2-methylhexane is at m/z 43 (M-57)43:13
- Mass Spectra of Alkenes45:42
- Mass Spectra of Alkenes: Remove 1 e⁻45:43
- Mass Spectra of Alkenes: Fragment46:14
- High-Energy Pi Electron is Most Likely Removed47:59
- Mass Spectra of Aromatic Compounds49:01
- Mass Spectra of Aromatic Compounds49:02
- Mass Spectra of Alcohols51:32
- Mass Spectra of Alcohols51:33
- Mass Spectra of Ethers54:53
- Mass Spectra of Ethers54:54
- Mass Spectra of Amines56:49
- Mass Spectra of Amines56:50
- Mass Spectra of Aldehydes & Ketones59:23
- Mass Spectra of Aldehydes & Ketones59:24
- McLafferty Rearrangement1:01:29
- McLafferty Rearrangement1:01:30
- Mass Spectra of Esters1:04:15
- Mass Spectra of Esters1:01:16
- Mass Spectrometry Discussion I1:05:01
- For the Given Molecule (M=58), Do You Expect the More Abundant Peak to Be m/z 15 or m/z 43?1:05:02
- Mass Spectrometry Discussion II1:08:13
- For the Given Molecule (M=74), Do You Expect the More Abundant Peak to Be m/z 31, m/z 45, or m/z 59?1:08:14
- Mass Spectrometry Discussion III1:11:42
- Explain Why the Mass Spectra of Methyl Ketones Typically have a Peak at m/z 431:11:43
- Mass Spectrometry Discussion IV1:14:46
- In the Mass Spectrum of the Given Molecule (M=88), Account for the Peaks at m/z 45 and m/z 571:14:47
- Mass Spectrometry Discussion V1:18:25
- How Could You Use Mass Spectrometry to Distinguish Between the Following Two Compounds (M=73)?1:18:26
- Mass Spectrometry Discussion VI1:22:45
- What Would be the m/z Ratio for the Fragment for the Fragment Resulting from a McLafferty Rearrangement for the Following Molecule (M=114)?1:22:46
21m 9s
- Intro0:00
- Sample Reagent Table0:11
- Reagent Table Overview0:12
- Calculate Moles of 2-bromoaniline6:44
- Calculate Molar Amounts of Each Reagent9:20
- Calculate Mole of NaNO₂9:21
- Calculate Moles of KI10:33
- Identify the Limiting Reagent11:17
- Which Reagent is the Limiting Reagent?11:18
- Calculate Molar Equivalents13:37
- Molar Equivalents13:38
- Calculate Theoretical Yield16:40
- Theoretical Yield16:41
- Calculate Actual Yield (%Yield)18:30
- Actual Yield (%Yield)18:31
16m 10s
- Intro0:00
- Definition of a Melting Point (mp)0:04
- Definition of a Melting Point (mp)0:05
- Solid Samples Melt Gradually1:49
- Recording Range of Melting Temperature2:04
- Melting Point Theory3:14
- Melting Point Theory3:15
- Effects of Impurities on a Melting Point3:57
- Effects of Impurities on a Melting Point3:58
- Special Exception: Eutectic Mixtures5:09
- Freezing Point Depression by Solutes5:39
- Melting Point Uses6:19
- Solid Compound6:20
- Determine Purity of a Sample6:42
- Identify an Unknown Solid7:06
- Recording a Melting Point9:03
- Pack 1-3 mm of Dry Powder in MP Tube9:04
- Slowly Heat Sample9:55
- Record Temperature at First Sign of Melting10:33
- Record Temperature When Last Crystal Disappears11:26
- Discard MP Tube in Glass Waste11:32
- Determine Approximate MP11:42
- Tips, Tricks and Warnings12:28
- Use Small, Tightly Packed Sample12:29
- Be Sure MP Apparatus is Cool12:45
- Never Reuse a MP Tube13:16
- Sample May Decompose13:30
- If Pure Melting Point (MP) Doesn't Match Literature14:20
8m 17s
- Intro0:00
- Melting Point Tubes0:40
- Melting Point Apparatus3:42
- Recording a melting Point5:50
22m
- Intro0:00
- Crystallization to Purify a Solid0:10
- Crude Solid0:11
- Hot Solution0:20
- Crystals1:09
- Supernatant Liquid1:20
- Theory of Crystallization2:34
- Theory of Crystallization2:35
- Analysis and Obtaining a Second Crop3:40
- Crystals → Melting Point, TLC3:41
- Supernatant Liquid → Crude Solid → Pure Solid4:18
- Crystallize Again → Pure Solid (2nd Crop)4:32
- Choosing a Solvent5:19
- 1. Product is Very Soluble at High Temperatures5:20
- 2. Product has Low Solubility at Low Temperatures6:00
- 3. Impurities are Soluble at All Temperatures6:16
- Check Handbooks for Suitable Solvents7:33
- Why Isn't This Dissolving?!8:46
- If Solid Remains When Solution is Hot8:47
- Still Not Dissolved in Hot Solvent?10:18
- Where Are My Crystals?!12:23
- If No Crystals Form When Solution is Cooled12:24
- Still No Crystals?14:59
- Tips, Tricks and Warnings16:26
- Always Use a Boiling Chip or Stick!16:27
- Use Charcoal to Remove Colored Impurities16:52
- Solvent Pairs May Be Used18:23
- Product May 'Oil Out'20:11
19m 7s
- Intro0:00
- Step 1: Dissolving the Solute in the Solvent0:12
- Hot Filtration6:33
- Step 2: Cooling the Solution8:01
- Step 3: Filtering the Crystals12:08
- Step 4: Removing & Drying the Crystals16:10
25m 54s
- Intro0:00
- Distillation: Purify a Liquid0:04
- Simple Distillation0:05
- Fractional Distillation0:55
- Theory of Distillation1:04
- Theory of Distillation1:05
- Vapor Pressure and Volatility1:52
- Vapor Pressure1:53
- Volatile Liquid2:28
- Less Volatile Liquid3:09
- Vapor Pressure vs. Boiling Point4:03
- Vapor Pressure vs. Boiling Point4:04
- Increasing Vapor Pressure4:38
- The Purpose of Boiling Chips6:46
- The Purpose of Boiling Chips6:47
- Homogeneous Mixtures of Liquids9:24
- Dalton's Law9:25
- Raoult's Law10:27
- Distilling a Mixture of Two Liquids11:41
- Distilling a Mixture of Two Liquids11:42
- Simple Distillation: Changing Vapor Composition12:06
- Vapor & Liquid12:07
- Simple Distillation: Changing Vapor Composition14:47
- Azeotrope18:41
- Fractional Distillation: Constant Vapor Composition19:42
- Fractional Distillation: Constant Vapor Composition19:43
24m 13s
- Intro0:00
- Glassware Overview0:04
- Heating a Sample3:09
- Bunsen Burner3:10
- Heating Mantle 14:45
- Heating Mantle 26:18
- Hot Plate7:10
- Simple Distillation Lab8:37
- Fractional Distillation Lab17:13
- Removing the Distillation Set-Up22:41
28m 51s
- Intro0:00
- Chromatography0:06
- Purification & Analysis0:07
- Types of Chromatography: Thin-layer, Column, Gas, & High Performance Liquid0:24
- Theory of Chromatography0:44
- Theory of Chromatography0:45
- Performing a Thin-layer Chromatography (TLC) Analysis2:30
- Overview: Thin-layer Chromatography (TLC) Analysis2:31
- Step 1: 'Spot' the TLC Plate4:11
- Step 2: Prepare the Developing Chamber5:54
- Step 3: Develop the TLC Plate7:30
- Step 4: Visualize the Spots9:02
- Step 5: Calculate the Rf for Each Spot12:00
- Compound Polarity: Effect on Rf16:50
- Compound Polarity: Effect on Rf16:51
- Solvent Polarity: Effect on Rf18:47
- Solvent Polarity: Effect on Rf18:48
- Example: EtOAc & Hexane19:35
- Other Types of Chromatography22:27
- Thin-layer Chromatography (TLC)22:28
- Column Chromatography22:56
- High Performance Liquid (HPLC)23:59
- Gas Chromatography (GC)24:38
- Preparative 'prep' Scale Possible28:05
20m 50s
- Intro0:00
- Step 1: 'Spot' the TLC Plate0:06
- Step 2: Prepare the Developing Chamber4:06
- Step 3: Develop the TLC Plate6:26
- Step 4: Visualize the Spots7:45
- Step 5: Calculate the Rf for Each Spot11:48
- How to Make Spotters12:58
- TLC Plate16:04
- Flash Column Chromatography17:11
34m 25s
- Intro0:00
- Extraction Purify, Separate Mixtures0:07
- Adding a Second Solvent0:28
- Mixing Two Layers0:38
- Layers Settle0:54
- Separate Layers1:05
- Extraction Uses1:20
- To Separate Based on Difference in Solubility/Polarity1:21
- To Separate Based on Differences in Reactivity2:11
- Separate & Isolate2:20
- Theory of Extraction3:03
- Aqueous & Organic Phases3:04
- Solubility: 'Like Dissolves Like'3:25
- Separation of Layers4:06
- Partitioning4:14
- Distribution Coefficient, K5:03
- Solutes Partition Between Phases5:04
- Distribution Coefficient, K at Equilibrium6:27
- Acid-Base Extractions8:09
- Organic Layer8:10
- Adding Aqueous HCl & Mixing Two Layers8:46
- Neutralize (Adding Aqueous NaOH)10:05
- Adding Organic Solvent Mix Two Layers 'Back Extract'10:24
- Final Results10:43
- Planning an Acid-Base Extraction, Part 111:01
- Solute Type: Neutral11:02
- Aqueous Solution: Water13:40
- Solute Type: Basic14:43
- Solute Type: Weakly Acidic15:23
- Solute Type: Acidic16:12
- Planning an Acid-Base Extraction, Part 217:34
- Planning an Acid-Base Extraction17:35
- Performing an Extraction19:34
- Pour Solution into Sep Funnel19:35
- Add Second Liquid20:07
- Add Stopper, Cover with Hand, Remove from Ring20:48
- Tip Upside Down, Open Stopcock to Vent Pressure21:00
- Shake to Mix Two Layers21:30
- Remove Stopper & Drain Bottom Layer21:40
- Reaction Work-up: Purify, Isolate Product22:03
- Typical Reaction is Run in Organic Solvent22:04
- Starting a Reaction Work-up22:33
- Extracting the Product with Organic Solvent23:17
- Combined Extracts are Washed23:40
- Organic Layer is 'Dried'24:23
- Finding the Product26:38
- Which Layer is Which?26:39
- Where is My Product?28:00
- Tips, Tricks and Warnings29:29
- Leaking Sep Funnel29:30
- Caution When Mixing Layers & Using Ether30:17
- If an Emulsion Forms31:51
14m 49s
- Intro0:00
- Step 1: Preparing the Separatory Funnel0:03
- Step 2: Adding Sample1:18
- Step 3: Mixing the Two Layers2:59
- Step 4: Draining the Bottom Layers4:59
- Step 5: Performing a Second Extraction5:50
- Step 6: Drying the Organic Layer7:21
- Step 7: Gravity Filtration9:35
- Possible Extraction Challenges12:55
For more information, please see full course syllabus of Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry Reactions of Alkenes
Alkenes can undergo many reactions, including electrophilic additions like hydrohalogenations, where the pi bond breaks and a hydrogen and halogen are added according to Markovnikov’s rule, which is based on the stability of the carbocation intermediate. Hydration is another reaction of alkenes, where a hydrogen and OH group are added across the double bond in the presence of strong acid. Oxymercuration-demercuration and hydroboration-oxidation are alternative methods of hydrating alkenes. Other reactions of alkenes include bromination through the anti-addition of Br₂ and halohydrin formation. The catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes and dienes can also occur, as well oxidation, epoxidation, dihydroxylation, ozonolysis, radical addition, and polymerization. This lecture also offers tips on using flashcards and discussions of the regiochemistry and stereochemistry of the above reactions.
Share this knowledge with your friends!
Copy & Paste this embed code into your website’s HTML
Please ensure that your website editor is in text mode when you paste the code.(In Wordpress, the mode button is on the top right corner.)
- - Allow users to view the embedded video in full-size.










































 Answer Engine
Answer Engine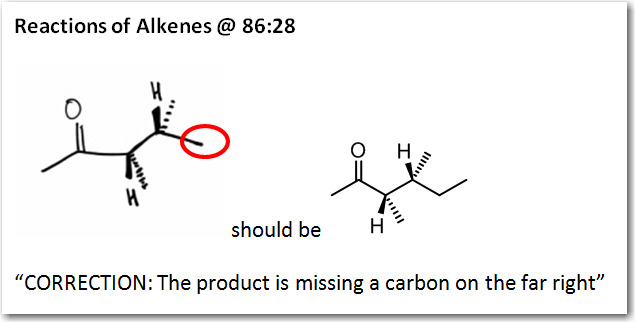
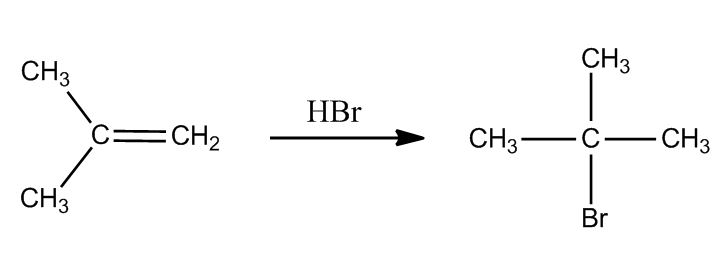
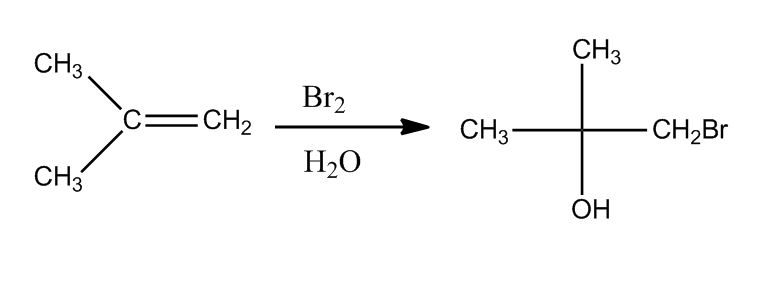
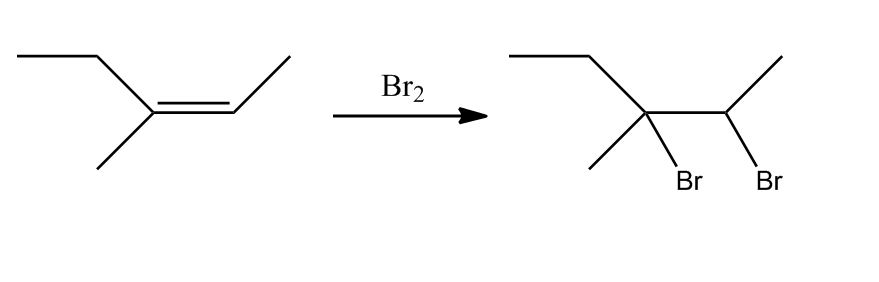
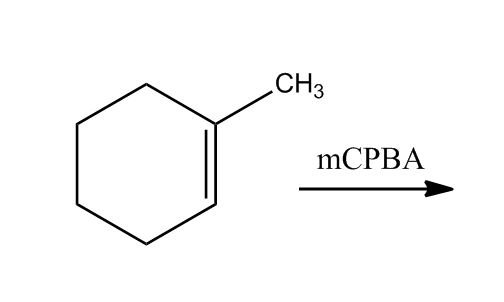
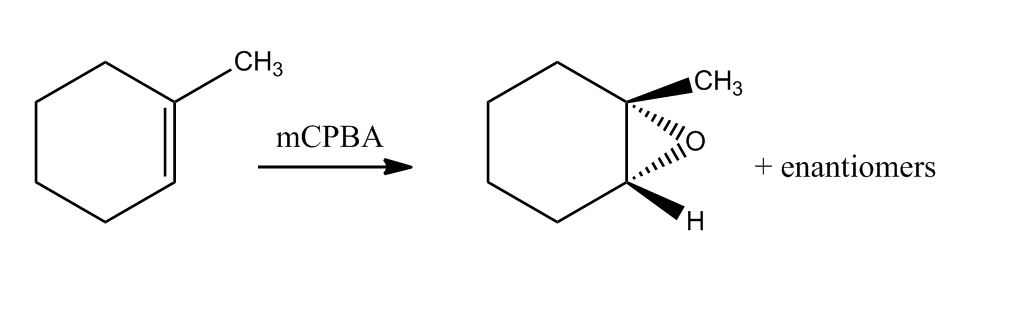
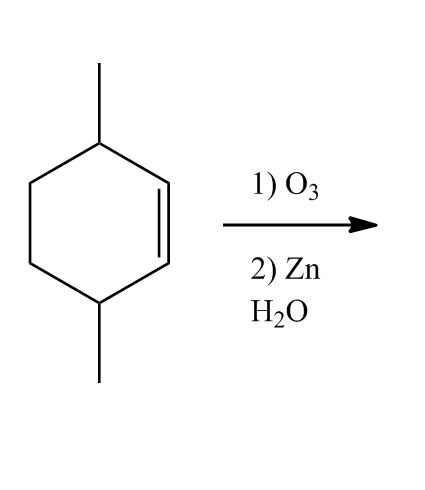
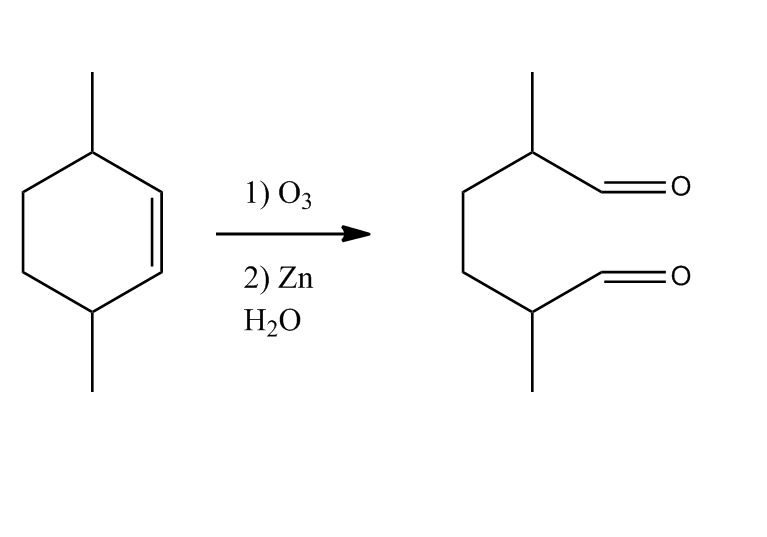
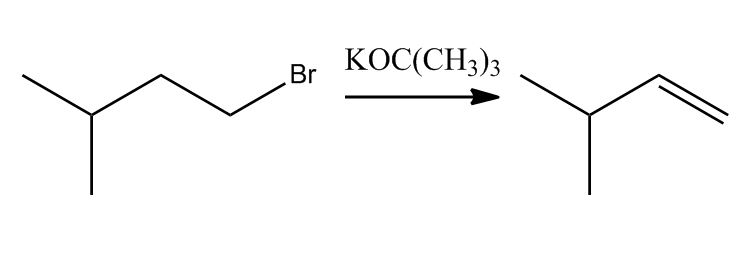
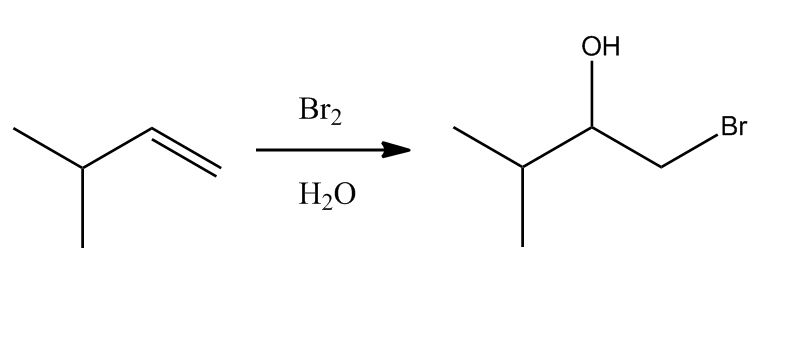
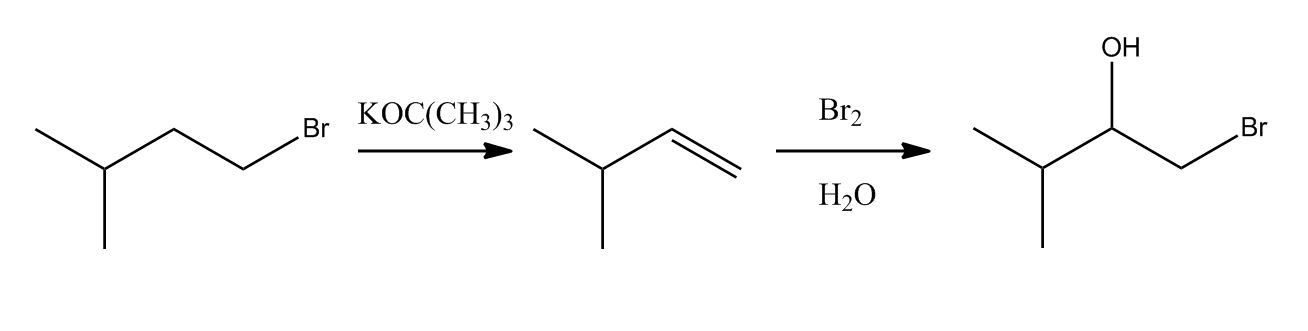








2 answers
Last reply by: Alex Ramirez
Wed Mar 23, 2016 3:48 AM
Post by Alex Ramirez on March 19, 2016
Hello Professor Starkey,
I'm asked a question about naming the alkene and reagents needed to synthesize 3-methyl-1,2-butanediol and I'm having a hard time. The question gives me that the products are racemic so I know that the alkene needs to be trans, and that I'll be using Osmium tetroxide for the synthesis, but in order for the hydroxyl groups to be at C1 and C2, it would need to be a tertiary alkene and I don't understand how to make enantiomers out of that from syn addition if it isn't technically a trans molecule. I guess I'm asking if you could walk me through the stereochemistry of the reaction?
Thank you very much
2 answers
Last reply by: Jason Smith
Wed Jan 13, 2016 8:09 PM
Post by Jason Smith on January 12, 2016
Hi professor. In the electrophilic addition mechanism for alkenes, why does the double bond break at all to allow the substitutions to take place? Why doesn't, say, a single bond break? Thank you professor.
3 answers
Sun May 3, 2015 8:59 PM
Post by Rene Whitaker on May 1, 2015
I'm having a sudden case of "stupid". At 18:22, when H20 acts as the nucleophile and attacks the carbocation, you get the H2O+. Great, but that is a good LG. So why does it "hang around" to get deprotonated rather than quickly leaving?
1 answer
Sat Dec 20, 2014 10:29 PM
Post by Parth Shorey on December 20, 2014
If you have HBR and ROOR, and then you have ROH and HBR what happened to the other RO when doing radical addition?
1 answer
Sat Dec 20, 2014 9:44 PM
Post by Parth Shorey on December 20, 2014
I still don't understand at 102:14 for KMn04. Where does the hydrogen come in to form the alcohols? So far I understand how the oxygen is formed through the stepwise mechanism but how do they become alcohols? Through KMn04?
3 answers
Sun Dec 14, 2014 8:30 PM
Post by Parth Shorey on December 11, 2014
At 23:40 why didn't you just add another bond after Ch3? Like a picture like this ?
OH
\-----\. /H
CH2 Sorry tried my best, I hope you understand my question?
1 answer
Sat Dec 6, 2014 9:08 PM
Post by Okwudili Ezeh on December 5, 2014
In thee hydration of alkenes, can't you use HS04- to deprotonate in the final step?
2 answers
Last reply by: Adriana Amerson
Sat Nov 29, 2014 6:18 PM
Post by Adriana Amerson on November 24, 2014
At 86:28, on the first example product given, where did the ethyl group go? I see it in the second example product, but not on the first.
1 answer
Fri Nov 21, 2014 5:45 PM
Post by Brijae Chavarria on November 19, 2014
Hi Dr. Starkey,
How would you approach a molecule that has two pi bonds when making an epoxide? In other words, how will we which pi bond to build the epoxide on? Thanks
1 answer
Thu Oct 9, 2014 12:22 AM
Post by Torrey Poon on October 8, 2014
Dr. Starkey, will you have anti-Markovnikov if you have an internal alkene?
2 answers
Last reply by: somia abdelgawad
Wed May 7, 2014 11:38 AM
Post by somia abdelgawad on May 6, 2014
hi professor: I was wondering what is the sterochemistry for the three kind of hydration of alkene. is it syn addition or anti addition?
1 answer
Fri Apr 25, 2014 12:36 AM
Post by Tina Cooper on April 18, 2014
Great Lecture. Dr. Starkey; I'm a little confused at 24:27. Here you said that the secondary benzylic carbon is more stable than just the secondary carbon. However, could be have done a 1,2 alkyl or hydride shift and seen that the carbon right below it is a tertiary thus more stable than the other two aforementioned?
1 answer
Wed Feb 19, 2014 12:14 PM
Post by Razia Chowdhry on February 19, 2014
You're lectures are amazing. I can't believe you kept on going so smoothly for 2 hours straight. Thank you again.
1 answer
Thu Nov 15, 2012 12:55 AM
Post by amina gangat on November 13, 2012
In the first example of oxymercuration you added a hg and oh, then replaced the hg with a h. In the second example of synthesis utility of alternate methods, you added an h, and replaced the hgoac with a oh. Can you please clarify on this? What am i supposed to add, and what do I replace hgoac with?
1 answer
Last reply by: Yun Seon Heo
Sun Oct 28, 2012 6:24 PM
Post by Yun Seon Heo on October 28, 2012
Hello Dr. Starkey, I was wondering if i can get lecture notes. All of them are so useful information so I want to have them but writing everything by hand delays me too much to finish one lecture.. Is there any way I can get the lecture note? Thanks
2 answers
Last reply by: Jessica Martinez
Thu Oct 4, 2012 2:14 PM
Post by Jessica Martinez on October 3, 2012
Hi. Dr. Starkey 8:21, is the rate determining step the same as the rate limiting step?
1 answer
Wed Aug 29, 2012 10:39 AM
Post by kwasi agyeman on August 28, 2012
Hi Pro. Starkey I cannot get pass the 6:33 the lecture resets back to the begining
1 answer
Thu May 10, 2012 7:17 PM
Post by Marina Iskander on May 7, 2012
In your catalytic hydrogenation "predict product" example when you did the syn addition of the two hydrogens your first product was missing a methyl at the end? why is that?
1 answer
Thu Apr 12, 2012 11:28 PM
Post by Annmarie Telemaque on April 12, 2012
can you show an example with1- methyl -cyclohexene with br2/h2O
1 answer
Sun Sep 25, 2011 7:37 PM
Post by Jamie Spritzer on September 25, 2011
what does the term "hot basic kmno4" mean? When you react an alkene with kmno4, do you get different products depending on whether you use hot basic kmno4 or cold, dilute kmno4?
Is the hot basic kmn04 always followed with an acid wash?
1 answer
Sat Jul 30, 2011 12:16 AM
Post by Joshua P on June 5, 2011
Hi Dr. Starkey, when do you plan to include more Organic videos, specifically on NMR? If you're unsure, please respond to this & let me know. Thank you.
1 answer
Last reply by: Joshua P
Sun Jun 5, 2011 5:53 PM
Post by Jamie Spritzer on May 30, 2011
Why are more substituted carbocations more stable?
0 answers
Post by Billy Jay on March 19, 2011
@108:00 Hmmm. I wonder where Dr. Starkey stores her money, haha.
I couldn't agree more with the person above me. Among all the topics I've seen taught here, you are by far the most effective and helpful teacher on here. Organic has always been a pain for me, but after watching this series of lectures, I was surprised to find out how fun Organic Chemistry can be. My whole outlook on Organic has changed because of you, so thank you.
0 answers
Post by Damien Leitner on March 13, 2011
I am currently studying for the MCAT and your lecture series has been incredibly helpful. I have taken OChem before in my BSc, and this is an excellent review! I feel like I've gone through an entire year of OChem in just over a month. Thank you Dr. Starkey for your indepth lectures and clearly stated demonstrations in each!