Connecting...

This is a quick preview of the lesson. For full access, please Log In or Sign up.
For more information, please see full course syllabus of College Calculus: Level II
For more information, please see full course syllabus of College Calculus: Level II
College Calculus: Level II Comparison Test
Lecture Description
In this video se are going to talk about the Comparison Test. The way this works is that we will be given a series that we are going to call an, and we create our own series that we will call bn. Then we will try to compare these two series to each other. So, first, we are going to talk about how to determine when the given series converges and when it diverges using the Comparison Test. We will see some examples that illustrate what happens when the test goes the right way and the wrong way. Then we are going to talk about second test called the Limit Comparison Test and see how it works.
Bookmark & Share
Embed
Share this knowledge with your friends!
Copy & Paste this embed code into your website’s HTML
Please ensure that your website editor is in text mode when you paste the code.(In Wordpress, the mode button is on the top right corner.)
×
Since this lesson is not free, only the preview will appear on your website.
- - Allow users to view the embedded video in full-size.
Next Lecture
Previous Lecture










































 Answer Engine
Answer Engine and
and  are series with positive terms. (
are series with positive terms. (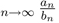 = some finite, positive (not 0) number.
= some finite, positive (not 0) number.






1 answer
Thu Aug 4, 2016 6:02 PM
Post by Peter Ke on July 30, 2016
For example 3, why can't we go straight to testing if the exponent is bigger than or less than 1 instead of wasting time doing the limit comparison test?
1 answer
Thu Apr 24, 2014 6:18 PM
Post by Brandyn Albrecht on April 22, 2014
Quick question. taking an/bn is just to figure out if the series are similar or whatever in terms of divergence, but for example 1 just to double check I took (1/n+1)/1/n and got n/(n+1) which converges to 1, which is a positive real number, which means an and bn should act similarly right? But they don't because an is smaller than bn, so does the an/bn approach only work for more confusing questions like example 3, and not for all questions in general?
3 answers
Tue Dec 17, 2013 9:09 PM
Post by Xenia Jeanty on November 30, 2013
lecture example 3 why is sqrt n/n same as 1/sqrt n? Can you please explain how did we get there?
1 answer
Tue Aug 13, 2013 5:24 PM
Post by charles daniel on July 24, 2013
lecture example 3 in the denominator n/n^2 should be equal to zero ..right?..why is it equal to one
1 answer
Tue Aug 13, 2013 5:21 PM
Post by charles daniel on July 24, 2013
lecture example 3 .. how is the bn of root(2n+17)/n become root n/n
1 answer
Tue Apr 16, 2013 8:27 PM
Post by Alena Schwartsman on April 14, 2013
Thank you Dr. Murray, concise and to the point. I like how you repeat the test's requirements with every example; easier to memorize the tests this way. Overall, I love how you explain things! Thank you again!
1 answer
Wed Apr 3, 2013 6:43 PM
Post by Rohail Tariq on April 1, 2013
cool
1 answer
Wed Apr 3, 2013 6:42 PM
Post by Ahmad Alshammari on September 13, 2011
why you put .. 3^(n-2) !!
1 answer
Wed Apr 3, 2013 6:34 PM
Post by Srinivasa Rao RAVELLA on April 14, 2011
how would you should tan(1/x) is convergent with the limit comparison test
1 answer
Wed Apr 3, 2013 6:26 PM
Post by Romin Abdolahzadi on April 4, 2011
Regarding the limit comparison test: If the limit is equal to 0, then if Bn converges then An also converges!