Connecting...

This is a quick preview of the lesson. For full access, please Log In or Sign up.
For more information, please see full course syllabus of Multivariable Calculus
For more information, please see full course syllabus of Multivariable Calculus
Multivariable Calculus Double Integrals
Lecture Description
In this lesson, we are going to start on a new topic. We are going to be talking about double integrals. The nice thing about this particular topic is you do not have to learn anything new. There is going to be some new notation, but in fact the notation itself is not even new. At the beginning, we are going to give a couple of quick definitions, and then we are just going to launch right into examples. We just want to be able to handle these problems and not worry about what is going on behind the scenes too much. You already know a lot of what is going on.
Bookmark & Share
Embed
Share this knowledge with your friends!
Copy & Paste this embed code into your website’s HTML
Please ensure that your website editor is in text mode when you paste the code.(In Wordpress, the mode button is on the top right corner.)
×
Since this lesson is not free, only the preview will appear on your website.
- - Allow users to view the embedded video in full-size.
Next Lecture
Previous Lecture










































 Answer Engine
Answer Engine
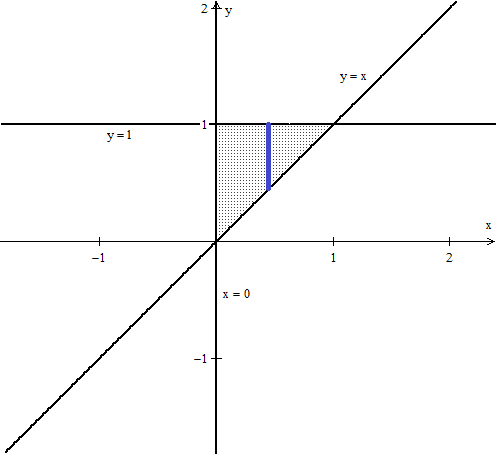
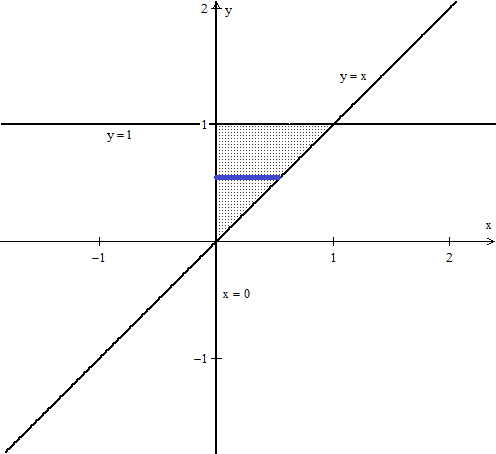




1 answer
Fri Aug 22, 2014 8:27 PM
Post by Denny Yang ♕ [Moderator] on August 19, 2014
Also in example 3, you made a minor calculation error. You wrote: The integral of(2x^3 - 12x^2 +19x, x, (3/2), 3 ). It should have been (2x^3 - 12x^2 +18x, x, (3/2), 3 ). The [ x, (3/2), 3 ] is the variable we are integrating and the lower bound and upper bound. Typing it just like you would on a Ti-89 Calculator.
1 answer
Fri Aug 22, 2014 8:23 PM
Post by Denny Yang ♕ [Moderator] on August 19, 2014
Q. ii) Integrate ∫ − π\protect\mathord/ \protect phantom π2 / 20 ey dx.
What is this?
1 answer
Mon May 13, 2013 12:53 AM
Post by Josh Winfield on May 12, 2013
Hello Raffi,
Can you just clarify why in example 3 you put the limit of integration for dx as (3-y) on the bottom and (y) on the top. I had them the other way around but im wrong but i cant figure out why?
0 answers
Post by Justin Dehorty on February 23, 2013
How do I find the Lower and Upper Sums? Apparently this is another way to calculate double integrals, but I don't understand how to set up the sigmas properly.
1 answer
Sat Dec 29, 2012 5:01 PM
Post by Alexander Rekitsanov Alexander Rekitsanov on December 15, 2012
I think that the region the prof is integrating is wrong in example 3. in the question it is stating that region that is bounded by y=0 ,y=x and y=-x+3 but the prof ignores the y=0 part. isn't the region suppose to be the left triangle in the drawing ? please if you could clarify it, thank you.